Memoria de largo
plazo
Name the character
Type in the name of the character whose change throughout the story you are going to analyze.
Example: Nick Carraway.
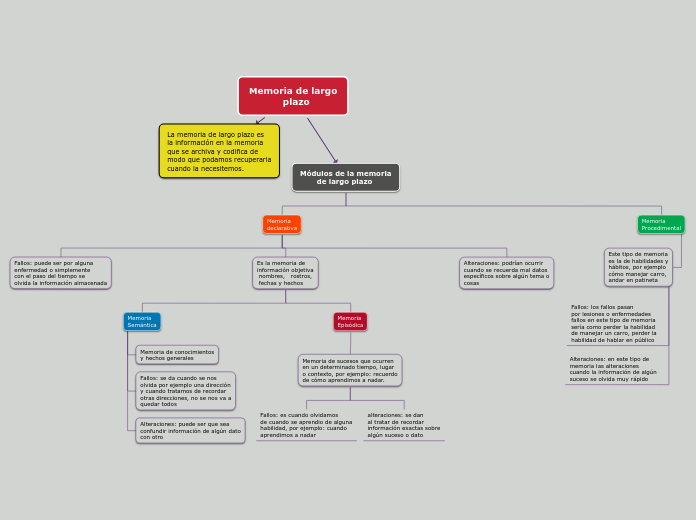
La memoria de largo plazo es
la información en la memoria
que se archiva y codifica de
modo que podamos recuperarla
cuando la necesitemos.
Módulos de la memoria
de largo plazo
Character's behavior
Think of the character's behavior at the beginning of the story and look for the way it changed throughout the story.
Memoria
Procedimental
Este tipo de memoria
es la de habilidades y
hábitos, por ejemplo
cómo manejar carro,
andar en patineta
Change in behavior
How did the character change the first behavior you mentioned? Type in a quote to prove your statement.
Example: Nick assumes the whole responsibility for Gatsby's funeral arrangements, 'with that intense personal interest to which every one has some vague right at the end.'
Alteraciones: en este tipo de
memoria las alteraciones
cuando la información de algún
suceso se olvida muy rápido
Fallos: los fallos pasan
por lesiones o enfermedades
fallos en este tipo de memoria
sería como perder la habilidad
de manejar un carro, perder la
habilidad de hablar en público
Memoria
declarativa
Alteraciones: podrían ocurrir
cuando se recuerda mal datos
específicos sobre algún tema o
cosas
Es la memoria de
información objetiva
nombres, rostros,
fechas y hechos
Memoria
Episódica
Memoria de sucesos que ocurren
en un determinado tiempo, lugar
o contexto, por ejemplo: recuerdo
de cómo aprendimos a nadar.
alteraciones: se dan
al tratar de recordar
información exactas sobre
algún suceso o dato
Fallos: es cuando olvidamos
de cuando se aprendio de alguna
habilidad, por ejemplo: cuando
aprendimos a nadar
Memoria
Semántica
Alteraciones: puede ser que sea
confundir información de algún dato
con otro
Fallos: se da cuando se nos
olvida por ejemplo una dirección
y cuando tratamos de recordar
otras direcciones, no se nos va a
quedar todos
The reason for the change in behavior
What caused the character to change the first behavior you mentioned? Type in the reason for the change.
Example: 'because no one else was interested ', and he felt Gatsby shouldn't be left alone in his last moments.
Memoria de conocimientos
y hechos generales
The reason for the change in behavior
Type in the explanation for the character's change of behavior.
Example: He became so involved with dishonest and careless people that he began to resemble them.
Fallos: puede ser por alguna
enfermedad o simplemente
con el paso del tiempo se
olvida la información almacenada
Initial behavior
How does the character act at the beginning of the story? Type in a relevant quote for your statement.
Example: Nick shows his immature side as he leaves to New York in order to avoid 'being rumored into marriage' with his girlfriend.