Observing experiments
Failure - Prediction is wrong
Success - Prediction is correct
Make a prediction
Floating topic
The seven SI base units, which are comprised of:
- Length - meter (m)
- Time - second (s)
- Amount of substance - mole (mole)
- Electric current - ampere (A)
- Temperature - kelvin (K)
- Luminous intensity - candela (cd)
- Mass - kilogram (kg)
/system-of-units-with-names-605777630-5ab29b28a474be00193f2a4d.jpg)
Basic Safety Rules:
- Know locations of laboratory safety showers, eyewash stations, and fire extinguishers. The safety equipment may be located in the hallway near the laboratory entrance.
- Know emergency exit routes.
- Avoid skin and eye contact with chemicals
- Minimize all chemical exposures.
- No horseplay will be tolerated.
- Assume that all chemicals of unknown toxicity are highly toxic.
- Post warning signs when unusual hazards, hazardous materials, hazardous equipment, or other special conditions are present.
- Avoid distracting or startling persons working in the laboratory.
- Use equipment only for its designated purpose
- Combine reagents in their appropriate order, such as adding acid to water.
- Avoid adding solids to hot liquids.
- All laboratory personnel should place emphasis on safety and chemical hygiene at all times.
- Never leave containers of chemicals open.
- All containers must have appropriate labels. Unlabeled chemicals should never be used.
- Do not taste or intentionally sniff chemicals.
- Never consume and/or store food or beverages or apply cosmetics in areas where hazardous chemicals are used or stored.
- Do not use mouth suction for pipetting or starting a siphon.
- Wash exposed areas of the skin prior to leaving the laboratory.
- Long hair and lose clothing must be pulled back and secured from entanglement or potential capture.
- No contact lenses should be worn around hazardous chemicals even when wearing safety glasses.
- Laboratory safety glasses or goggles should be worn in any area where chemicals are used or stored. They should also be worn any time there is a chance of splashes or particulates to enter the eye.
- Closed-toe shoes must be worn at all times in the laboratory. Perforated shoes or sandals are not appropriate.
- Determine the potential hazards and appropriate safety precautions before beginning any work.
- Procedures should be developed that minimize the formation and dispersion of aerosols.
- If an unknown chemical is produced in the laboratory, the material should be considered hazardous.
- Do not pour chemicals down drains, and do not utilize the sewer for chemical waste disposal.
- Keep all sink traps (including cup sink traps and floor drains) filled with water by running water down the drain at least monthly.
- Do not utilize fume hoods for evaporations and disposal of volatile solvents.
- Perform work with hazardous chemicals in a properly working fume hood to reduce potential exposures.
- Avoid working along in a building. Do not work alone in a laboratory if the procedures being conducted are hazardous.
- The permissable exposure limit (PEL) and the threshold limit values (TLV) must be observed in all areas. If exposure above a PEL or TLV is suspected for an ongoing process, please contact EHS immediately.
- Laboratory employees should have access to a chemical inventory list, applicable safety data sheets (SDS), departmental laboratory safety manual, and relevant standard operating procedures.
- Access to laboratories and support areas such as stockrooms or specialized laboratories should be limited to approved personnel only.
- All equipment should be regularly inspected for wear or deterioration.
- Equipment should be maintained according to the manufacturer's requirements and records of certification, maintenance, or repairs should be maintained for the life of the equipment.
- Designated and well-marked waste storage locations are necessary.
- No cell phone or ear bud usage is allowed in the active portion of the laboratories or during experimental operations.
- Clothing made of synthetic fibers should not be worn while working with flammable liquids or when a hazard is present as these materials tend to melt and stick to exposed skin.
- Laboratory coats should not be stored in offices or break rooms as this spreads contaminates to other areas.
- Computers and instrumentation should be labeled to indicate whether gloves should be worn or not. Inconsistent glove use around keyboards is a source of potential contamination.
- Avoid wearing jewelry in the lab as this can post multiple safety hazards.
A Bunsen burner:
- named after Robert Bunsen, is a kind of ambient air gas burner used as laboratory equipment; it produces a single open gas flame, and is used for heating,
Triple Beam Balance:
- The triple beam balance is an instrument used to measure weight very precisely.
Graduated Cylinder:
- is a common piece of laboratory equipment used to measure the volume of a liquid.
Summary
Summary of the Scientific Method
- Make an observation. toaster.
- Ask a question.
- Propose a hypothesis.
- Make predictions.
- Test the predictions.
- Conclusion of Your Results
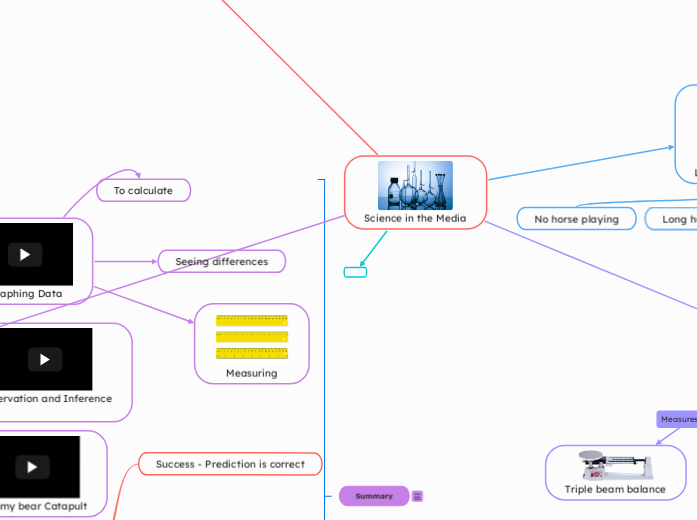
Science in the Media
Lab Science safety
wear goggles
Long hair needs to be pulled back
No horse playing
Unit of Measurement
Liquid measurements
Scientific Method
Gummy bear Catapult
Built Catapult
6 elastic bands, 7 popscicle sticks, tape and paper cup
Launched them
Decided which one was best
Observed which went furthest
Make predictions about which would go farthest
Observation and Inference
Graphing Data
Seeing differences
Measuring
To calculate
Lab Equipment

Bunsen burner
Graduated Cylinder
Triple beam balance


/system-of-units-with-names-605777630-5ab29b28a474be00193f2a4d.jpg)




