av priyusha tollimalli för 5 årar sedan
648
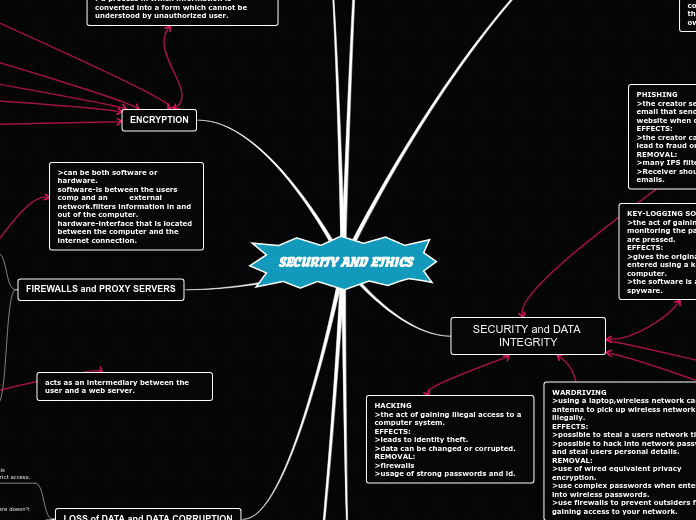
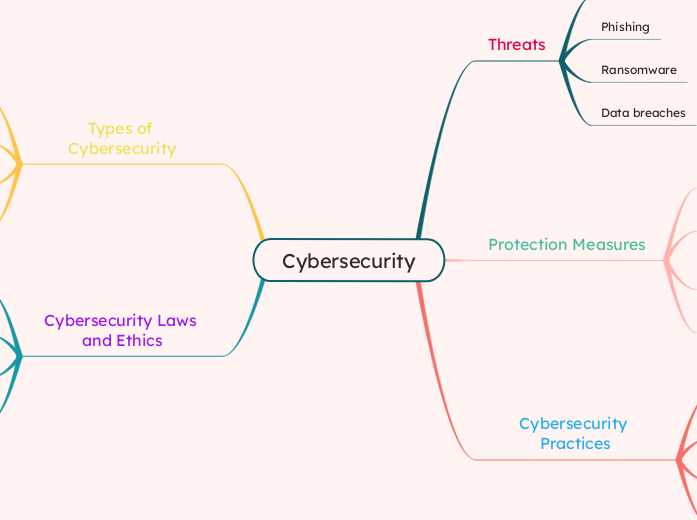
SECURITY AND ETHICS
The provided text explains various key concepts related to internet security and software. It details that freeware is software available for free download but does not allow users to modify its source code.