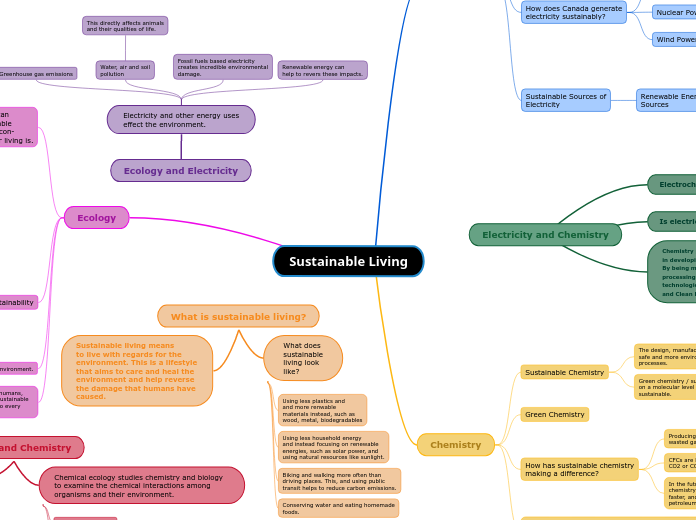
Ecology and Chemistry
Chemical Ecology
Species-specific chemicals are large forming factors in community processes.
ex. population dynamics
ex. selective feeding
ex. niche structure
ex. seasonal succession
Helps to understand terrestrial ecosystems.
Chemical ecology studies chemistry and biology to examine the chemical interactions among organisms and their environment.
Communication between individuals
ex. hormone responses
Signaling processes
Ecology and Electricity
Electricity and other energy uses
effect the environment.
Renewable energy can
help to revers these impacts.
Fossil fuels based electricity
creates incredible environmental
damage.
Water, air and soil
pollution
This directly affects animals
and their qualities of life.
Greenhouse gas emissions
What is sustainable living?
Sustainable living means
to live with regards for the
environment. This is a lifestyle
that aims to care and heal the
environment and help reverse
the damage that humans have
caused.
What does
sustainable
living look
like?
Conserving water and eating homemade
foods.
Biking and walking more often than
driving places. This, and using public
transit helps to reduce carbon emissions.
Using less household energy
and instead focusing on renewable
energies, such as solar power, and
using natural resources like sunlight.
Using less plastics and
and more renwable
materials instead, such as
wood, metal, biodegradables
Electricity and Chemistry
Chemistry plays a large contributing role
in developing new materials for renewable energy.
By being more energy efficient in the chemical processing industries, and by advancing cleaner fuel technologies, chemistry will help meet the Affordable and Clean Energy goal.
Is electricity a chemical reaction?
Electricity is not a chemical reaction,
but chemical reactions are used to
procure electricity.
Electrochemistry
An area of chemistry that describes the connections
between electricity and chemical change. Some
chemical reactions produce energy. Small reactions
like these can be found in batteries and fuel cells in
order to create electric power.
Sustainable Living
Ecology
Ecology is the study of living organisms, including humans, and their relations to their physical environment. Sustainable living and environmental impacts relate directly into every component of ecology.
How sustainable our living is affects
physical environment, which affects how
animals live in them. Our ways of living describe
our relationship with our physical environment
and decide how other species interact with their
changing environment in order to adapt.
Sustainability is ultimately for the environment.
Ecological Sustainability
Long-lived and healthy forests are examples of sustainable biological systems.
It means to reduce human impacts on the natural environment and people's health to a degree that is manageable and survivable for both the natural environment and humanity.
Ecological sustainability is the conservation of productivity of things like water, soil and the ecosystem.
Ecological sustainability includes everything related to the Earth's ecosystems.
Where electricity and chemistry can
be aimed in encouraging sustainable
living, the environment sees the con-
sequences of how sustainable our living is.
When we try to live more sustainably and
take the environment into account, there
can be positive effects.
We see life thrive
Less pollution
Less polluted soil
More drinkable water
Less toxic airs
When we don't live sustainably, our ways of
living destroy the environment.
Unlivable circumstances
Soil, water and
air pollution
Poor air quality
Soil erosion
Habitat destruction
Global warming
Deforestation
Animal extinction
Chemistry
In our chemistry class, we also looked at
the production of plastics, their molecular structure
and the consequences of their creation and slow biodegradability.
How has sustainable chemistry
making a difference?
In the future, through ongoing science and studies,
chemistry will be able to break down PET plastics
faster, and hopefully find an alternative to
petroleum-based plastics.
CFCs are being replaced with naturally occurring
CO2 or CO2 byproducts in polystyrene foam sheets.
Producing fuel and other useful chemicals out of
wasted gas.
Green Chemistry
Sustainable Chemistry
Green chemistry / sustainable chemistry involves innovating
on a molecular level in terms of being more green and sustainable.
The design, manufacture and use of efficient, effective,
safe and more environmentally friendly chemical products and processes.
Electricity
Sustainable Sources of
Electricity
Renewable Energy
Sources
Wave/Tide
Wind and Solar
Geothermal
Biomass
Hydroelectricity
How does Canada generate
electricity sustainably?
Wind Power
Wind power is electricity produced by converted
kinetic energy from turbines.
Nuclear Power
Nuclear power is created from a process that
generates heat by nuclear fission. The consequential
steam rotates a turbine that generates electricity.
Hydropower
Hydropower is the use of flowing water to
generate electricity.
How do you save electricity to live
more sustainably?
Use a Green-e electrical supplier if possible.
Find non-electrical ways to keep yourself
cool/warm during extreme temperatures
instead of heating the house or turning air
conditioning on.
Open the window and use natural daylight
as a source of light rather than turning the
lights on.
Ensure to turn appliances off or pull the plug
so that the currents isn't constantly running.
Use timers and smart heating
controls to help regulate electricity
usages.