Textile Recycling and Reuse
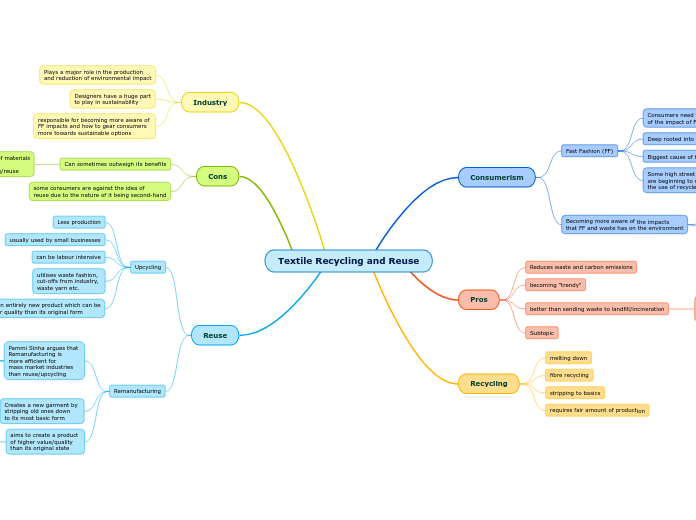
Reuse
Remanufacturing
aims to create a product
of higher value/quality
than its original state
aims to extend the warranty/
lifespan of materials & fibres
Creates a new garment by
stripping old ones down
to its most basic form
Pammi Sinha argues that
Remanufacturing is
more efficient for
mass market industries
than reuse/upcycling
"higher form of reuse that
focuses on value-added
recovery"
quicker production rate
less labour intensive
Upcycling
creates an entirely new product which can be
of a lower quality than its original form
utilises waste fashion,
cut-offs from industry,
waste yarn etc.
can be labour intensive
usually used by small businesses
Less production
Cons
some consumers are against the idea of
reuse due to the nature of it being second-hand
Can sometimes outweigh its benefits
i.e. transportation of materials
can outweigh the
benefits of recycling/reuse
Industry
responsible for becoming more aware of
FF impacts and how to gear consumers
more towards sustainable options
Designers have a huge part
to play in sustainability
Plays a major role in the production
and reduction of environmental impact
Recycling
requires fair amount of production
stripping to basics
fibre recycling
melting down
Pros
Subtopic
better than sending waste to landfill/incineration
It is argued that reuse is better
than recycling since it has a lower
production rate
becoming "trendy"
Reduces waste and carbon emissions
Consumerism
Becoming more aware of the impacts
that FF and waste has on the environment
Tends to be the younger generation
consumers are gearing more
towards eco-friendly & recycled
fashion & textiles
Fast Fashion (FF)
Some high street brands
are beginning to move towards
the use of recycled materials & fibres
Biggest cause of fashion/textile waste
Deep rooted into the fashion world
Consumers need to be aware
of the impact of FF