av Sandhu Priya för 1 månader sedan
77
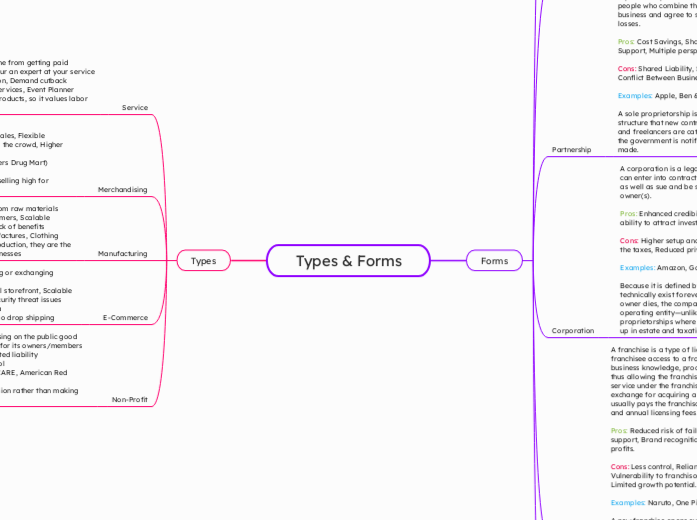
Types & Forms
Different business structures offer various advantages and disadvantages that cater to the needs of individual entrepreneurs and groups. Partnerships involve collaboration between two or more individuals who share resources, risks, profits, and liabilities, often benefiting from cost savings and diverse perspectives but facing potential conflicts and shared control.