av nursyafeera azeera för 12 årar sedan
1020
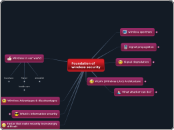
wireless Network security
Information security is a multi-layered approach involving products, people, and procedures. This framework ensures the protection of devices that store, manipulate, and transmit data.