作者:Azzie Bennett 10 月以前
260
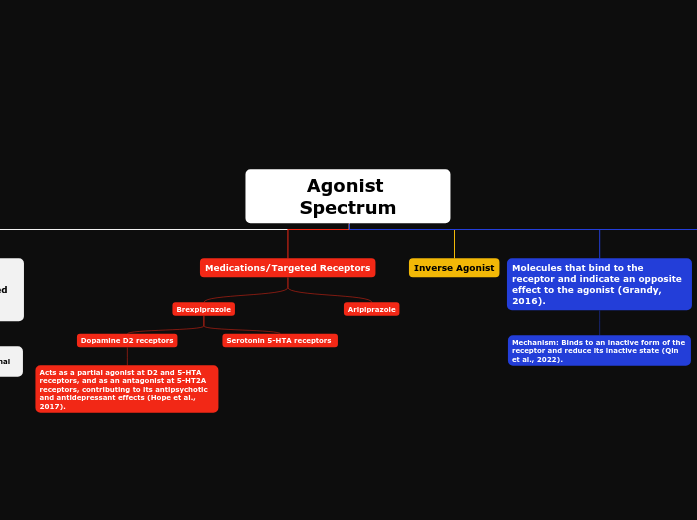
Agonist Spectrum - Logic Chart
In pharmacology, molecules that interact with receptors can be classified based on their effects. Agonists bind to receptors and activate them, producing a full response. Partial agonists also bind to receptors but induce a less pronounced effect compared to full agonists.