aprendizaje auditivo
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
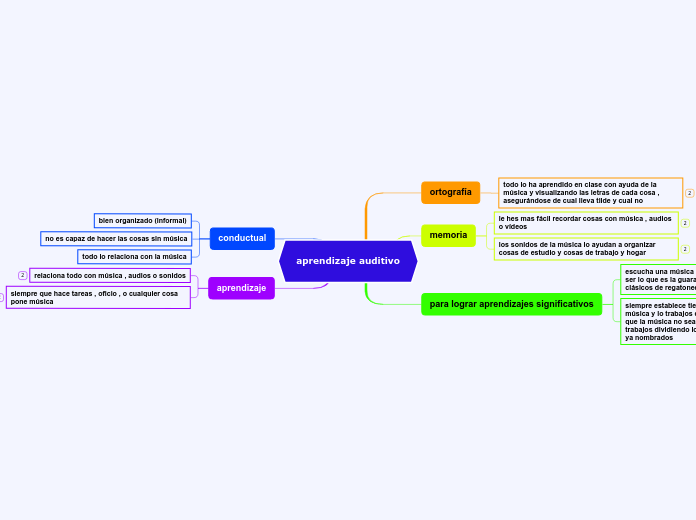
aprendizaje
A conjunction is a word like 'if' 'but' or 'and' which is used to connect sentences or clauses together.
siempre que hace tareas , oficio , o cualquier cosa pone música
Subordinating conjunctions are conjunctions that are used at the beginning of subordinate clauses. Some examples of these conjunctions are: although, after, before, because, how, if, once, since, so that, until, unless, when etc.
Although it was raining, I went out.
relaciona todo con música , audios o sonidos
Coordinating conjunctions always connect phrases, words, and clauses. They are: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so.
This stew is savory and delicious.
conductual
An interjection is used to express emotion in a sentence.
Think of other interjections!
todo lo relaciona con la música
no es capaz de hacer las cosas sin música
bien organizado (informal)
para lograr aprendizajes significativos
A pronoun is a word that can be used in place of a noun, typically after the noun itself has already been stated.
siempre establece tiempo determinado entre la música y lo trabajos que se van a realizar haciendo que la música no sea la misma por horas o por trabajos dividiendo los diferentes estilos de musica ya nombrados
escucha una música en especial en particular puede ser lo que es la guaracha , salsa romántica y los clásicos de regatonee
Relative pronouns are used to add more information to a sentence. Which, that, who (including whom and whose), and where are all relative pronouns.
Which, Where
memoria
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
los sonidos de la música lo ayudan a organizar cosas de estudio y cosas de trabajo y hogar
Superlative adjectives demonstrate a higher level of comparison between entities.
She is the prettiest princess.
le hes mas fácil recordar cosas con música , audios o vídeos
Expresses a comparison between two entities or groups of entities in quality or degree.
He is taller than she is.
ortografía
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
todo lo ha aprendido en clase con ayuda de la música y visualizando las letras de cada cosa , asegurándose de cual lleva tilde y cual no
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
Create sentences
Cats, Rain