BASES CONCEPTUALES DE LA PEDAGOGÍA
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order.
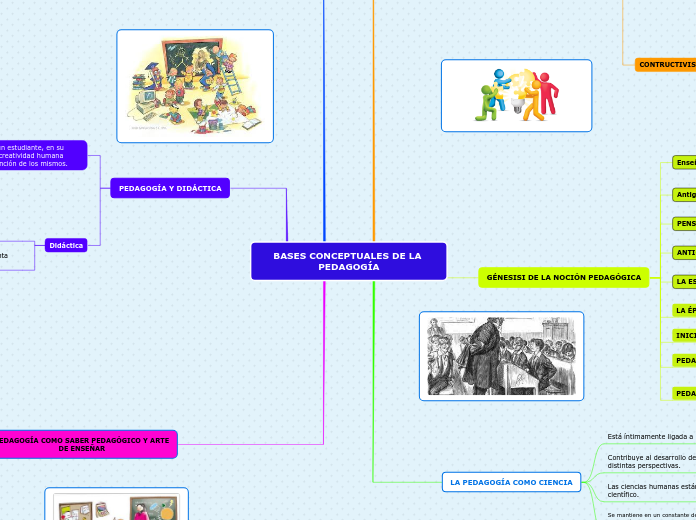
PEDAGOGÍA COMO SABER PEDAGÓGICO Y ARTE DE ENSEÑAR
Para su desarrollo será importante combatir contra la educación estandarizada que contiene el materialismo y la visión científica.
Uno de sus objetivos es prepara a la comunidad educativa para el futuro y adaptarla a cambios artísticos.
El docente debe incentivar al docente a desarrollar actividades artísticas, para aumentar su potencial.
Canaliza la sensibilidad en niños y adolescentes.
Fortalece la creatividad y permite la adaptación a distintas asignaturas como matemáticas o lenguaje.
Potencia el trabajo intelectual, además de brindar un sentido de pertinencia e identidad.
PEDAGOGÍA Y DIDÁCTICA
A compound sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses joined by a comma, semicolon or conjunction. An independent clause is a clause that has a subject and verb and forms a complete thought.
Didáctica
Create your own compound sentences, using the coordinators above.
El el arte práctico de enseñar, que toma en cuenta los procesos disciplinarios de forma sistemática.
Son los medios que facilitan el desarrollo y la compresión del proceso educativo
El éxito del aprendizaje de un estudiante, en su mayor parte depende de la creatividad humana necesaria para captar la atención de los mismos.
When independent clauses are joined with coordinators (also called coordinating conjunctions), commas and semicolons, they do more than just join the clauses. They add meaning and flow to your writing.
Relación estudiante - docente
Conocer al estudiante
Noción vigilante
Desafío
Experiencia
Educabilidad
Para evitar el fracaso escolar es importante considerar los siguientes aspectos:
PEDAGOGÍA Y EDUCACIÓN
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.
ELEMENTOS DEL PROCESO EDUCATIVO
An appositive clause follows another noun or noun phrase in apposition to it; that is, it provides information that further identifies or defines it.
Los resultados de aprendizaje
Destrezas, habilidades, capacidades tanto físicas como cognitivas adquiridas mediante el proceso educativo y la metodología pedagógica
El educador
PEDAGOGO
The subject clause is a dependent clause that acts as a subject.
Es aquella persona encargada de reinventar métodos o técnicas, válidas para que los estudiantes aprendan de forma autónoma y libre, más conocido como profesor.
El estudiante
Persona beneficiada a quien se imparte educación, suele a travesar su proceso con el acompañamiento de su maestro.
Contenidos
Material de estudio planificado de acuerdo a objetivos, para alcanzar saberes escolares.
Contexto educativo
Es uno de los elementos en el que participa la educación.
PEDAGOGÍA
A predicative clause may be introduced by conjunctions - that, whether, whether... or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way - or connectives.
The latter may be conjunctive pronouns - who, whoever, what, whatever, which - or conjunctive adverbs - where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why.
La pedagogía es el proceso que permite que la educación hoy en día sea un realidad.
Es la ciencia que estudia los métodos o recursos aplicados para el pleno ejercicio de la educación y su desarrollo.
EDUCACIÓN
The object clause is a phrase on which a verb performs an action. It falls at the end of a sentence, and is governed by a verb or a preposition.
Se dice que es la puerta al éxito o a la superación.
Es aquel proceso que permite alcanzar habilidades y conocimientos para desempeñarse en distintos ámbitos que presente la vida.
LA PEDAGOGÍA COMO CIENCIA
Se mantiene en un constante debate ya que al estudiar a la educación que si es una ciencia dificulta su entendiemiento como la misma.
Las ciencias humanas están limitadas por el método científico.
Contribuye al desarrollo del potencial humano desde distintas perspectivas.
Está íntimamente ligada a la vida del ser humano.
GÉNESISI DE LA NOCIÓN PEDAGÓGICA
PEDAGOGÍA MODERNA XIX
Cambios notables en el proceso de educación desde las relaciones entre estudiantes y maestros hasta métodos de impartir educación.
PEDAGOGÍA TRADICIONAL XVII Y XVIII
Impone de forma rígida costumbres y tradiciones de sumisión
INICIO DE LA DIDÁCTICA XVI
Principios de la didáctica.
LA ÉPOCA DEL HUMANISMO XVI
Batallaban para que el conocimiento se esparciera por la humanidad.
LA ESCOLÁSTICA XII
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is driving the red car.
Fundación de la escuela como el lugar donde se construían saberes.
ANTIGUA ROMA VII
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is driving the car with his mother.
Papel de maestro Alumno, y el proceso de enseñanza era a través de los métodos Trivíum y Quadrivium.
PENSAMIENTO OCCIDENTAL V
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim is the driver.
Creación de la escuela del pensamiento por algunos filósofos.
Antiguo Oriente y la Antigua Grecia 3000a.C
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives the car.
Establecieron los primeros medios de enseñanza
Enseñanza primitiva
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives.
Transmisión de conocimientos entre padre e hijos, para saciar necesidades o realizar actividades básicas.
CONFIGURACIÓN EPISTÉMICA DE LA PEDAGOGÍA
CONTRUCTIVISMO
Traditional grammar defines the object in a sentence as the entity that is acted upon by the subject.
El sujeto y el objeto son entes fundamentales del proceso educativo.
La persona es la protagonista del proceso educativo.
The indirect object identifies the person/thing for whom/which the action of the verb is performed.
The indirect object is usually a person or a thing.
El desarrollo del conocimiento depende de la organización mental de un individuo.
The direct object is the receiver of the action mentioned in the sentence.
Add example
Constructivismo crítico
La realidad de la persona y del entorno pertenecen al conocimiento.
Constructivismo radical
Hace referencia a nuestras inherentes transformaciones apreciaciones.
EPISEMOLOGÍA EN LAS CIENCIAS DE LA EDUCACIÓN
The predicate of a sentence is the part that modifies the subject in some way. Because the subject is the person, place, or thing that a sentence is about, the predicate must contain a verb explaining what the subject does and can also include a modifier.
CORRIENTES DEL PENSAMIENTO
Ciencia como actividad esencialmente cognitiva.
Neutralidad del investigador.
Operacionalismo
Conocimiento producido por hechos.
Carácter atomizado del conocimiento
Relaciona datos o estadísticas.
Inducción y deducción.
Operaciones mentales generadoras de conocimiento.
Metologismo e instrumentalismo.
Consecuencia de la metodología.
Dualismo epistemológico.
Comprende el conocimiento
Monismo epistemológico.
Explica e interpreta el conocimiento.
POSTURAS EMPÍRICAS:
DIALÉTICA
Relación entre sujeto y objeto, conocimiento en constante evolución.
RELACIONISTA
Tiene conocimientos a priori.
EMPÍRICA
Conocimiento originado de forma progresiva.
La epistemología en la educación estudia de manera crítica y reflexiva el proceso educativo para encontrar problemas en cuanto a bases científicas.
EPISTEMOLOGÍA
The subject of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb.
Ask the question, 'Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?' and the answer to that question is the subject.
Detecta problemas en la pedagogía, los cuales deben ser solucionados por los pedagogos o investigadores de la educación.
En pedagogía, la epistemología es aquel instrumento que ayuda a estudiar las ciencias de la educación.
Es la herramienta utilizada para analizar la generación del conocimiento y su vinculación con la ciencia y su metodología, además de ser parte de la filosofía.