Biome Concept Map
Tundra
The threats that are affecting the grasslands is due to climate change and the things that take place in the biome have in impact on the surrounding environment.
Global warming
- Causes permafrost to melt and with methane being released it speeds up the process

Oil, drilling sites, pipelines, mines and military bases damage the soil and vegetation in the grasslands and because of the extreme cold temperature the vegetation and soil take years to renew it-self.

In the Tundra the natural resources are fossils, oil, gold and coal.
Fossils
- Valuable fossils like from the woolly mammoth were found among others.

Oil
- The oil is extracted but when it occurs it has an impact on the surrounding environment.

The tundra is one of the coldest, harshest biomes on the Earth. There are only a few selected groups that live here.
Inuits
- Also known as Eskimos are the largest group that live in the Canadian Arctic and Greenland in the tundra. They live along the cost and hunt caribou, seal, and fish.
Innu
- Located in the northern Labrador and Quebec tundra regions
Yakut
- They live in Siberia tundras. They hunt and fish and change locations twice a year. They mainly have dairy, fish, vegetables, and meat.
Precipitation, temperature, permafrost, wind are abiotic factors for the Tundra biome.
Biotic Factors:
- Low Shrubs (sedges, reindeer mosses, liverworts, and grasses)
- Crustose and Foliose Lichen
- Herbivores (lemmings, voles, caribou)
- Carnivores (arctic foxes, wolves, polar bears)
- Migratory Birds (ravens, snow buntings, falcons, loons)
- Insects (mosquitoes, flies, moths, grasshoppers)
- Fish (cod, flatfish, salmon)
The tundra is mainly located in the Northern hemisphere covering the northern parts of North America, Greenland and Eurasia. The latitude and longitude is 71.2 degrees N and 156 degrees W.
Desert
Global warming
- Is increasing the occurrence of drought, which ends up drying up the water holes.
Wildfires
- Increasing temperatures produce an increasing number of wildfires.

Irrigation
- In the long-term lead to salt levels in the soil that might become too high to support plants.
Oil, natural gas and minerals are beneath the Sahara Desert.

Water is a vital natural resource and is a lifeline for people who live nearby.

There are 2.5 million people in the desert in the Sahara region of Africa.

Many of these people live in one place for a short amount of time and then move around in search of more productive land.

Many of the people in the Sahara keep cattle and form little farms where they grow as much food as they can to feed themselves and their family.
Biotic factors in the desert like plants and animals have specific adaptations that allow them to move through the sand, keep cool, and conserve water.
Precipitation, water availability, sunlight, and temperature are all abiotic factors.
Hot, dry landscape with intense sunlight are the abiotic factors of the desert.
The Rainshadow effect is an example of an abiotic factor..
The deserts that are located by mountains the "rainshadow" effect takes place. As air moves up over a mountain range, it gets cold and loses the ability to hold moisture, so it either rains or snows. When the air moves down to the other side of the mountain, it gets warmer. Warm air holds a lot of mositure, so it does not rain as much, as a result a desert has formed.

Scorpions, coyotes, snakes, spiders, lizard, and cacti, faunas are just a few of the biotic factors.
Most deserts are found in bands along the 30 degrees latitude N and 30 degrees S (Figure 1).
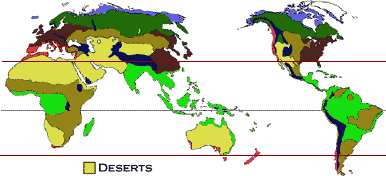
Figure 1 - This map of the world shows where the deserts are located along the red bands.
Savanna
Threats that are having an impact on the ecosystem is climate change, farming practices, overgrazing, aggressive agricultural irrigation, deforestation and erosion.

Aggressive agricultural irrigation
- Irrigation methods dry up life giving rivers and water holes.
Desertification
- Tropical savannas sometimes are close to being arid, desert regions and the spread of these desert like conditions into dry grassland areas.
The natural resources in the Savanna is grasses, oil, uranium, platinum, diamonds, coal, gold, and oil.

The people living in this biome are mainly farmers who grow cereals and other plants that can resist long dry spells.
Masai
- Is a variety of groups who share the same language and cultural and social similarities.
- They live scattered between Kenya and Tanzania.
The Bushman
- is another group who live in the Kalahari desert.
- Many of the original groups have disappeared or are reduced to few dozens of individuals so that now the Bushmen are only 10 – 15,000.
Climate, soil, topography, natural disturbances, and precipitation are all abiotic components.

Trees, grasses, shrubs, mosses and lichens are types of producers found in a savanna grassland and lions, zebras, antelpoe, rodents, and many birds are the consumers.
Savanna biomes are in Africa, South America, India and Australia.
Africa – Tropical grassland that has a latitude of 15 degrees N and 30 degrees; longitude 15 degrees W and 40 degrees W.
South America – Tropical savanna that are mainly found in Brazil, Colombia, and Venezuela. They are between the latitude of 3 to 10 degrees N and longitude of 62 to 74 degrees W.
India – the savanna here is a small piece of land in Terai–Duar at the bottom of the Himalayas reaching out 16 miles wide.
Australia – most are located near the equator but the Australian one is south of the equator.
Grassland
Humans are converting the grasslands into areas for grazing animals.

Fires constantly take place

Because of the amount of fertile soil, grasslands are being cleared by people for their crops.
The natural resources include water, lumber, wheat, coal, oil, corn, gas, and livestock.
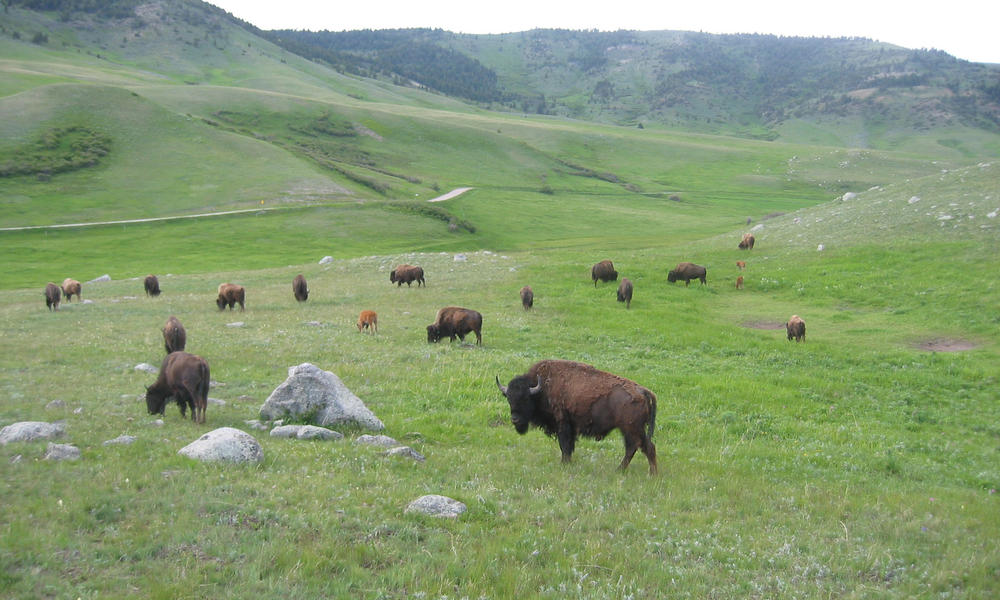

The natural services in grasslands are carbon sinks as the grass uses the carbon to perform photosynthesis.

About 800 million people live in grasslands.
Most of the original land has been turned into agricultural uses and urban areas.
Very few people live in the Steppe climate because of the harsh conditions. Farmers would have a hard time growing crops because the soil is so poor and its so cold.
Climate is one of the most crucial aboitic factors that shape the ecosystem and involves rainfall, temperature, wind flow and ground moisture.
Grasses, sedged, rushes, cyanobacteria. lichens, mosses, trees. praire dogs, bison, and different birds
Temperate grasslands are located throughout the world.
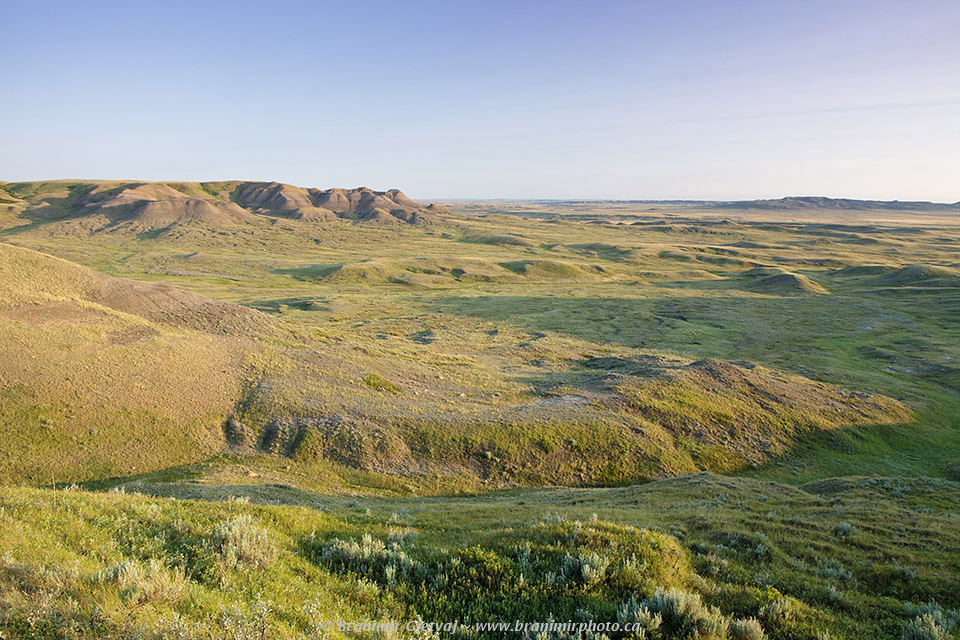

Nebraskan Grasslands – longitude is 95 W to 104 W and latitude is 40 N to 43 N.
Australian Grasslands – latitude is 33 S and longitude is 151 E
African Grasslands – latitude 30.5 S and longitude is 20 E.
Chaparral/Mediterranean
Fires, mudslies, flooding are threats to this biome.
Plants like Eucalyptus and Sagebrush produce resins and oils which we use for the pleasant aroma and flavor.
The human population in this biome doesn't have an exact number because this biome takes up most of southern California and most of it's entire coast plus islands off of the coast that have people on them.
In California, a main concern associated with the chaparral is the large human populations that live in and around this biome.
Abioic Features
Mountains, water, and rocks are abiotic factors of this biome
Biotic factors include foxes, ferns, trees, birds, ticks, broomrapes, pumas, coyotes, and rabbits.
The Chaparral biome is in many countries but is mainly found in California. Latitude is 35-40 N and longitude is 118-123 W.

Boreal/Taiga Forest
Extensive coal mining, logging, road building, oil, gas, and hydroelectric developments pose a threat to this biome.
The largest taiga biome is found in Russia and their natural resources is coal, oil, and natural gas. Along with it being mined for its aluminum ore and diamond deposits.
The sparse human population of 22 000 is 60% aboriginal.
Abiotic factors are..
- Sunlight
- Water
- Boulders
- Soil
- Clouds
- Lightning
- Hail
- Floods
- Temperature
Biotic factors are...
- Black Bear
- Bald Eagle
- Red Fox
- River Otter
- Wolverine
- Snowshoe Rabbit
- Balsam Fir
- Eastern Red Cedar
- White Poplar
- White Spruce
- Siberian Spruce
The taiga is located between 50 degrees and 60 degrees latitude N and the Arctic circle.

Temperate Deciduous Forest
Acid rain
- Caused by industrial and vehicular emissions (biggest threat to this biome).
- Damages tree leaves, trees produce fewer/smaller seeds, and reduces resistance.

Other threats include strip mining spread of invasive, non-native species competing for food and space, unsustainable forestry.

Climate chance is another major threat to temperate forest.
Trees
- are harvested for their wood like construction to boats and furniture
- Oak, beech, maple, chestnut, elm, basswood, sycamore, linden, walnut, and birch are the type of trees that are found there

Flora
- Guelder rose (a shrub), its bark is used in herbal medicine to treat conditions like asthma and the red berries from it is used instead of cranberries.
- Ferns are used by native Americans as an analgesic.

Most of the world's population lives in this temperate region.
Rocks, soil, water, sunlight, climate, rain, hills, temperature, and air masses.
Biotoic Features
Deer, rodents, large/ small birds, fox, common lime, lady fern, carpet moss, least weasle, oak trees, birch trees, decidious trees, chipmunks.
This biome is in Japan, southwest Russia, eastern China, South America, New Zealand, and southeastern Australia. The biome extends across the world in temperate areas at the latitudes of 45 degrees N and 45 degrees S.

Rainforest
Ecological Threats
Logging
~ rainforests are cut down so the trees can be used for flooring, furniture, and other items.

Agricultural interests
~ clear forests for cropland
Mining operations
~ clear forests to build roads and dig mines

Paper industry
~ turns large areas of rain forest trees into pulp
So the main ecological threat for rainforests is deforestation
Natural Resources
The land of rainforests is cleared for farming, mining, ranching, and timber projects.

Rainforests have many valuable resources for the human population. Resources are used for the industry, medicine, and food.
Industry: rubber, oils, gum, waxes, flavorings, and dyes
Medicine: many plants can provide cures for diseases (ex. Rosy periwinkle, the drug made from this plant can help cure children with leukemia)
Food: many grains and fruits

Human Population
Mbuti and Baka Pygmies are groups that live in the rainforests of Central Africa.
Traditionally they live by hunting and gathering food.
The Huli are one of the many tribes that live in the remote highland forests of Papua New Guniea.
Characteristics
The tropical rainforest is a biome with a constant temperature and a high degree of rainfall. Rainforest ecosystems have a unique water and nutrient cycle because of the level of humidity and density of the vegetation.

Abiotic Features
Abiotic factors are a non-living physical and chemical factor that have an impact on the surrounding environment. Abiotic factors create conditions that allow biotic factors to live and grow.

The abiotic factors in a tropical rain forest include precipitation, sunlight, soil nutrients, and temperature. The plants (biotic) depend on sunlight and soil nutrients (abiotic). In the rain forest organisms and populations depend on warm temperatures and water.
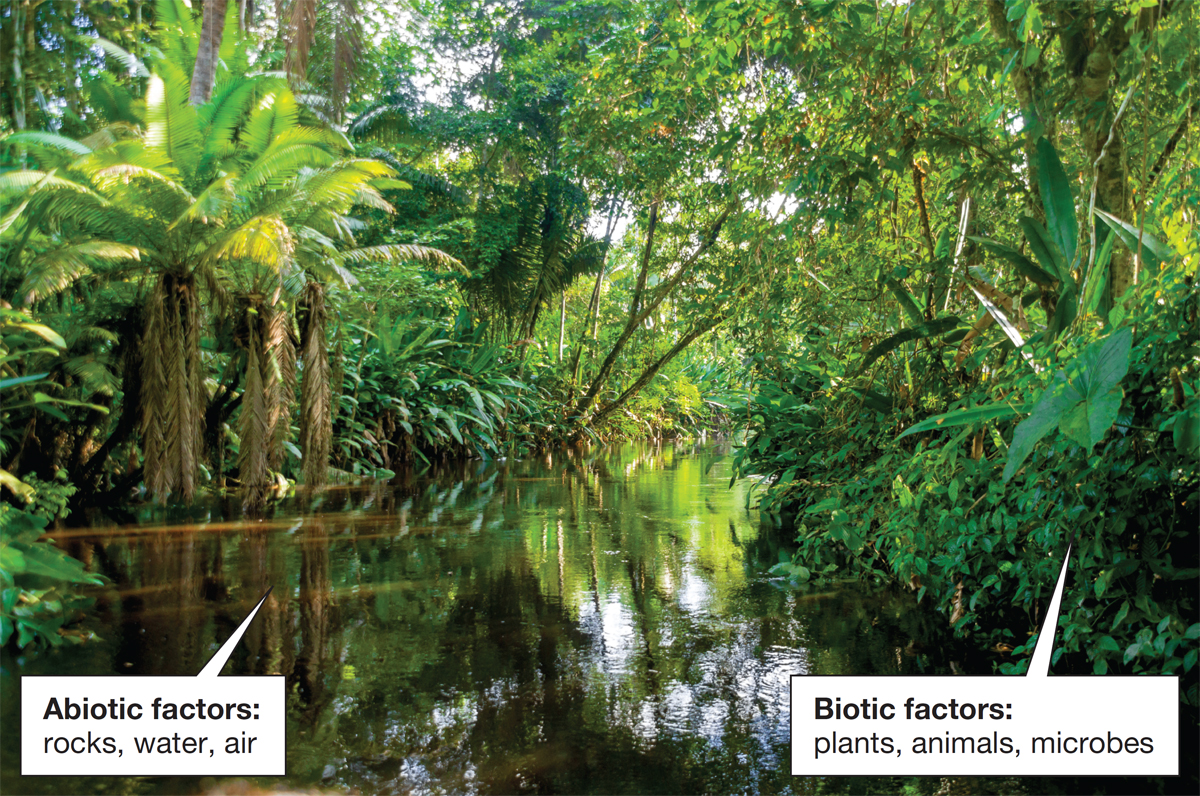

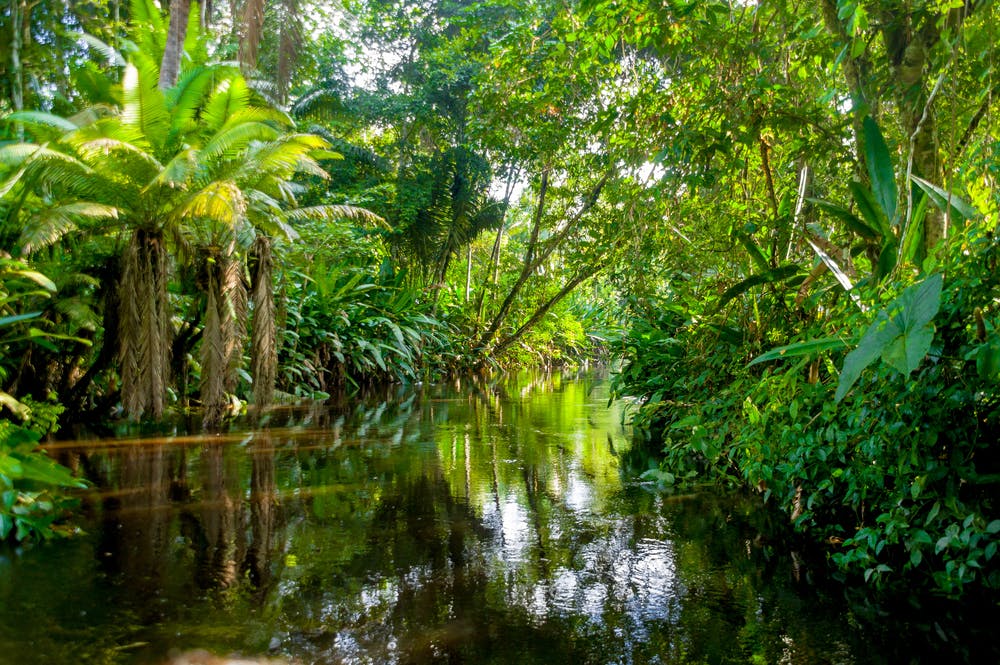
Biotic Features
Biotic factors are the living things in an ecosystem that have an impact on other living things and/or the environment

The biotic factors in the rainforests are producers (autotrophs), consumers (heterotrophs) and decomposers (detritivores). In the forest plants are mostly the producers, and organisms like fungi and earthworms are decomposers.

Location
Typically, rainforests are located around the equator (Zero degrees latitude), mainly between the Tropic of Cancer (23.5° N latitude) and the Tropic of Capricorn (23.5° S latitude). This expands 3,000 miles called the ‘tropics’.
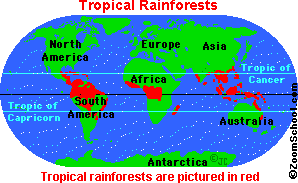
Large rainforests are in the Amazon River Basin (South America), the Congo River Basin (Western Africa), and Southeast Asia. Smaller rainforests are in Central America, Madagascar, Australia and other locations in the tropics.