Branches of Geography
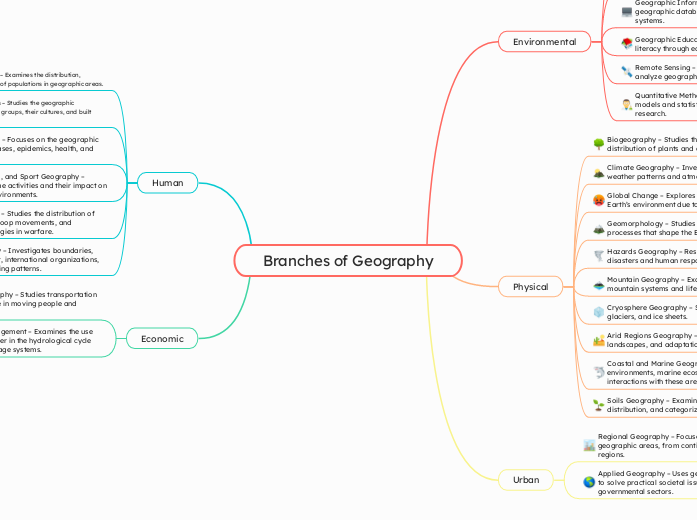
The study of geography encompasses a wide array of specialized fields that can be categorized into environmental, human, and physical geography. Environmental geography includes disciplines like cartography, which focuses on the art and science of map-making, and remote sensing, which employs satellite technology to analyze geographical features.
開啟
Branches of Geography Economic Water Resources Management – Examines the use and distribution of water in the hydrological cycle and human-made storage systems. Transportation Geography – Studies transportation networks and their role in moving people and goods. Human Political Geography – Investigates boundaries, nation development, international organizations, diplomacy, and voting patterns.
Military Geography – Studies the distribution of military facilities, troop movements, and geographical strategies in warfare. Recreation, Tourism, and Sport Geography – Analyzes leisure-time activities and their impact on local and global environments. Medical Geography – Focuses on the geographic distribution of diseases, epidemics, health, and healthcare access. Geography of Religions – Studies the geographic distribution of religious groups, their cultures, and built environments. Population Geography – Examines the distribution, migration, and growth of populations in geographic areas. Urban Applied Geography – Uses geographic knowledge to solve practical societal issues in private and governmental sectors. Regional Geography – Focuses on studying specific geographic areas, from continents to urban regions. Physical Soils Geography – Examines soil composition, distribution, and categorization. Coastal and Marine Geography – Studies coastal environments, marine ecosystems, and human interactions with these areas. Arid Regions Geography – Focuses on deserts, dry landscapes, and adaptation in arid climates.
Cryosphere Geography – Studies the Earth's ice, glaciers, and ice sheets.
Mountain Geography – Examines the formation of mountain systems and life in high altitudes.
Hazards Geography – Researches natural disasters and human responses to them. Geomorphology – Studies landforms and processes that shape the Earth's surface. Global Change – Explores long-term changes in the Earth’s environment due to human impacts. Climate Geography – Investigates long-term weather patterns and atmospheric activities. Biogeography – Studies the geographic distribution of plants and animals. Environmental Quantitative Methods – Applies mathematical models and statistical techniques to geographic research. Remote Sensing – Uses satellite and sensor data to analyze geographic features. Geographic Education – Enhances geographic literacy through education and research. Geographic Information Systems (GIS) – Develops geographic databases and digital mapping systems. Cartography – Focuses on map-making and improving geographic visualization. Agricultural and Rural Geography – Explores rural settlement, land use, and access to agricultural products.