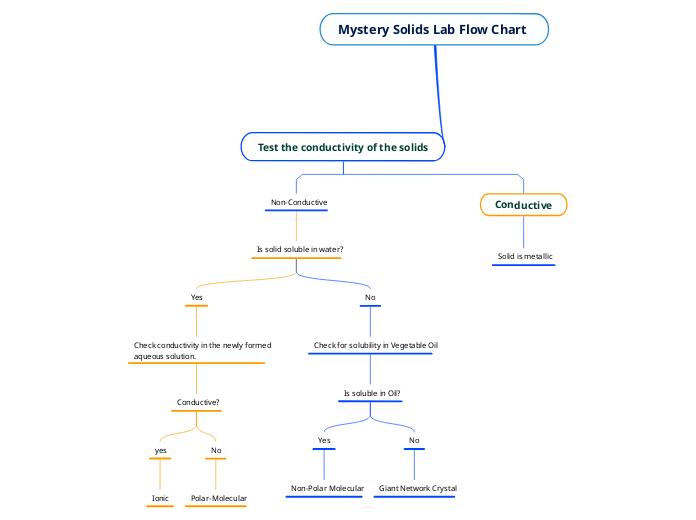
Nandni Dabhi
Phosphorus Trichloride
Most polyatomic ions are oxyacid which means that the acid/compound contains oxygen
Mono is only used on the second element, if the first element has one atom it would not use prefix.
part 2
Common molecules
NaCl
Sodium and chloride come together to form table salt which is used for everyday life also in mostly food.
CO2
One carbon and two oxygen come together to form carbon dioxide which is a harmful gas
Covalent bond
H20
2 hydrogen and one oxygen come together and form water which we use in everydaylife to stay hydrated, cook food, clean our body etc.
ionic compound
Chemical Nomenclature
Chemical Namings
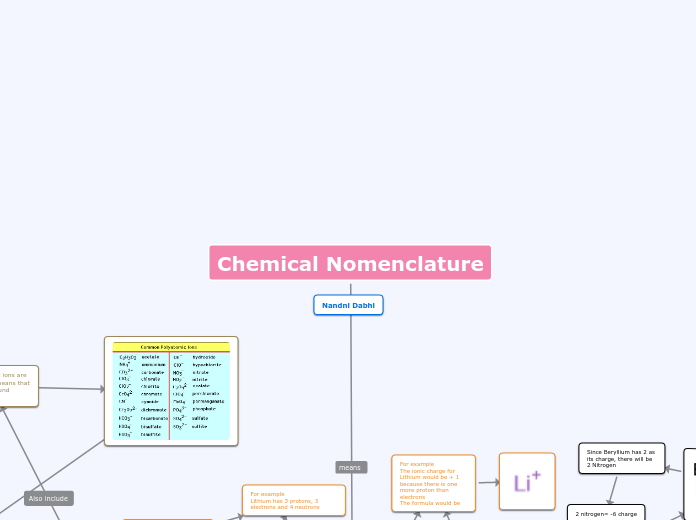
Ions
-Is a charged particle when the atom has gained or lost electrons
-The formula for an atom losing or gaining electron is called ionic charge
For example
The ionic charge for Lithium would be + 1 because there is one more proton than electrons
The formula would be
Atoms
For example
Lithium has 3 protons, 3 electrons and 4 neutrons
Is a subatomic particle that has an equal number of electrons and protons which makes it neutral
Criss-Cross method
The criss cross method does a simpler and easier way of writing the compound formula after understanding the concept.
Polyatomic ions
Binary acids
Binary acids are molecular compounds that is combined with the element hydrogen.
For example
Is a group of atoms with a charge
Multivalent ionic compound
Chemical names with transition metal have roman numeral numbers because it shows how much charge the atom has, since transition metals can have multiple charges.
Multivalent atoms are transition metals because they have more than one charge
Subtopic
These middle elements are called transition metals
Purple ones
Metals
metal ion
positive charge
Cation
a positively charged ion
Non-Metals
Non metal atoms
Non metal ion
negatively charged
Suffix
"-ide"
Only non metal atoms always have the suffix ending of ide at the end of every chemical name. (the suffix only applies to the non metallic atoms)
Anion
a negatively charged ion
Two non metals
Molecular compounds
formed with 2 or more non metals
Diatomics
these are molecules of only 2 atoms that can only be seen together
These diatmoic elements are only seen alone when they are in a a compound with another atom
Covalent bonds
Is a attraction that holds together 2 atoms which (only non metals
Prefixs
covalent compounds naming always starts with prefix in front on the element name to indicate how many atoms the compound consists of.
Ionic compound
Special cases
NO2 + H2O HNO3
Simplifying equations
C6H12O6
CH6O
6
Harder compounds
Barium nitride
Nitrogen
-3 electron charge
-6 electron charge with 2 nitrogen atoms
Barium
Both barium and nitrogen should have he same amount of charge in order for the elements to react with each other
2 electron charge
6 electron charge with 3 barium atoms
now both have equal amount of charges where the compound consists of 3 bariums and 2 nitrogen
Br3N2
Also known as a binary ionic
A mixture of two things
Ionic bonds
Is a attraction that would hold a positive and negative charged ions together in a compound. It's a transfer of electrons from a metal to a non metal.
Is a chemical bond or compound that is formed by two or more ions that are held together (metal ions and non-metal ions)
Naming compounds
How ionic compounds are formed