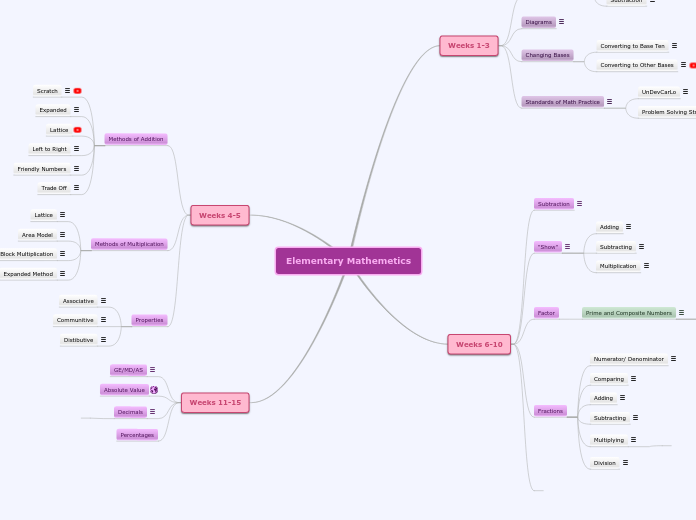
Elementary Mathemetics
Weeks 11-15
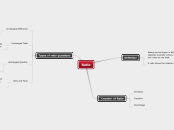
Advanced Area model

This is the basic area model
Now can we do it with unlike terms
Such as (2x+4)(4x+7)
Top left box would be: 8x^2
Top right box: 14x
Bottom left box: 16x
Bottom right box: 28
= 8x^2+30x+ 28
Diagonals always are like terms
Percentages
40% of 60
10% of 60=6
6 x 4= 24
45% of 60
10% = 6
x 4% =x4
____________
40% = 24
+ 5%= + 3
____________
45% = 27
Decimals
- The "show" for adding, subtracting, and multiplying decimals is very similar for the "show" for fractions
- you make one box for each
- you split it into 10
- adding you fill in the amount
- if it goes into the hundredths place you have to make it split into tenths horizontally, too
- for subtracting you cross out what you're taking away (just like fractions)
- and multiplying you count everything that's shaded with two colors
Absolute Value
GE/MD/AS
- Order of operation redone - GEM/DA/S
- G
- Grouping
- E
- Exponents
- M/D
- Multiple/Divide
- A/S
- Add/Subtract
Weeks 4-5
Properties
Distibutive
7(x*2)
6(5*4)
Communitive
Order doesn't matter
5 + 7 + 1 = 1 + 7 +5
Associative
Order stays the same
5 + (7 + 1) = (5 + 7) +1
Methods of Multiplication
Expanded Method
(157)(64)
100 + 50 + 7
x 60 + 4
______________
6000
3000
420
400
200
28
_______
10,048
Base Ten Block Multiplication
Area Model

Methods of Addition
Trade Off
35 33
+28 = +30
____ ____
63
47 46
+19 = +20
____ ______
66
Friendly Numbers
- Also called compatible numbers
- 36+18+42+24+17+11+43
36+18+42+24+17+11+43- 40+20+40+20+20+11+40
Left to Right
579
+864
________
1300
130
13
________
1443
- add hundreds spot, then tens, then one
Lattice
Expanded
243 200+40+3
+133 + 100+30+3
= 300+70+6 = 376
Scratch
Count to base then scratch
Weeks 6-10
Fractions
Division
Flip second fraction and multiply across
Multiplying
- When multiplying, only one box is used. Draw the box, draw the first set of lines per the first fraction, shade in the numerator, then add the second set of lines, shade in for the second fraction, count up how many boxes have both shading, and that's the answer over total amount of boxes.
- Ex: (1/2)(3/4)= 3/8
- When multiplying a fraction by a whole number, the first number is how many groups, and then the second number is how many is inside each group.
- Ex: 3 (1/3)
- 3 groups with 1/3 in each =1
- When subtracting, only two boxes are used, draw those two boxes and divide them up per the fraction, shade in the amount of the numerators, then draw the second line on each box, 'x' out the shading from the second box (second fraction, you're 'taking it' away), count the amount of boxes crossed out and crossed the same amount out from the first box, count up how many boxes are still shaded in the first box and that's your answer over how many total boxes
- Ex: 1/2 - 1/5 + 3/10
- If there's common denominator just add the numerators together
- Ex: 3/7 + 1/7 = 4/7
- When adding, draw two boxes and divide them up per the fraction, shade in the amount of the numerators, draw both lines on each box, count up how many boxes are shaded from each, then draw a third box to add up how many individual spaces are shaded in both original models.
- Ex: 1/4 + 2/3 = 11/12
Comparing
- Same Numerator
- 5/11 < 5/7
- a denominator of 7 is bigger pieces so 5 of those pieces is more than 5 of little pieces
- Same Denominator
- 5/7 > 2/7
- Anchor Fractions
- 4/9 < 6/11
- 4/9 is less than half, 6/11 is more than half
- ex: 1/2 , 1/4
Numerator/ Denominator
The numerator shows how many pieces you have and how big the pieces are
The Denominator shows how many total and how big they are
Factor
Prime and Composite Numbers
- Prime Numbers
- Numbers that only have exactly 2 factors
- Which are 1 and that number
- Ex: 2, 3, 5, 7, 11, 13
- Composite Numbers
- Every other number; numbers with more than 2 factors
- 4, 6, 9, 10, 12
Prime Factorization
Least Common Multiple
- The greatest number that two or more numbers are divisible by.
- Use greatest exponents for each number.
- Ex: 12 = 24, 36, 48, 60, 72 / 30 = 60, 90, 120, 150
- 60 is the Least Common Multiple
Greatest Common Factor
- The smallest number that goes into two or more numbers.
- Use smallest exponents for each number.
- Ex: 30 = 5x6, 3x10, 1x30, 2x15 / 12 = 2x6, 4x3, 1x12
- 6 is the Greatest Common Factor
"Show"
- Each number is represented by a + or - sign, depending on their sign, positive or negative.
- Positive and negative signs = zero pair; collection is a zero bank.
- Ex: + + +
- - -
- Can make as many zero pairs as desired/needed.
- SUBTRACT or TAKE AWAY is different from NEGATIVE.
- For multiplication, separate numbers into groups and units.
- Each group contains a number of positives or negatives.
- For negative numbers, TAKE AWAY groups of units.
Multiplication
- 3(2) =
- Create 3 groups of 2 positives
- (++) + (++) + (++)
- Answer = 6
-
- -3(-2) = (++(--) -->) + (++(--) -->) + (++(--) -->)
- Take away three groups of two negatives
- Left with only positives
- Answer = -6
Subtracting
- (-2) -5 = (--) - (+++++
- - - - - - )
- Take away the five positives created by zero bank
- (+++++) -->
- Left with seven negatives (-------)
- Answer = -7
- (-2)-(-1) = (--) - (-)
- Take away one negative (-) -->
- No need to create a zero bank
- Answer = -1
Adding
- 2+(-3) = (++) + (---)
- 3 + and 3 - create a zero bank
- + +
- - - -
- One - left over
- Answer = -1
- (-5)+(-3) = (-----) + (---)
- Add negatives together
- No zero bank
- Answer = -8
- Change one number to be a factor of ten
- Add same number to both sides.
- Subtract normally.
- Ex: 64-22 = 64(+8)-22(+8)
- 72-30 = 42
Weeks 1-3
Standards of Math Practice
- Make sense of problem and persevere
- Reason Abstractly/Quantitatively
- Construct Viable Arguments
- Use Appropriate Tools
- Look for & make sense of Structure
- Look for Repeated Reasoning
- Model
- Attend to Precision
Problem Solving Strategies
- Look for a Pattern
- Do a Similar/Easier Problem
- Identify What Makes the Problem Hard, and Get Rid of the Hard part.
- Draw a Diagram (units, longs, flats)
- Guess and Check
- Write an Equation
UnDevCarLo
- Understand the Problem
- Develop a Plan
- Carry out the Plan
- Look Back
Changing Bases
Converting to Other Bases
Base ten # Base five Base six Base Nine
8 13 12 8
12 22 20 13
19 34 31 21
41 131 105 45
Converting 8 into base five you have 1 long and 3 units which is 13 base five
Converting 19 into base six you have 3 longs and 1 unit which is 31 base six
Converting 41 into base nine take 41 divided by 9 which is 4 with 5 remaining, so 45 base nine
Converting 19 into base four . . . ~ . . . ~ . . . ~ . . . ~ . . .
. = 1 and ~ = a long, so that's 4 longs a 3 units which equal 43 base four
LLLLLLLLLeaving base 10 7|_152 =305 base seven
Converting to Base Ten
Multiply the number of Longs by the Base, then add the Units
34 base six = 22
3 longs plus 4 units, 3*6= 18 + 4= 22
423 base seven
4 (7^2) + 2 (7^1) + 3 (7^0)
4 (49) + 2 (7) +3
196 + 14 + 3
213
- any number to the power of zero is 1
132 base four
1 flat, 3 longs, 2 units
1(4^2) + 3(4^1) + 2(4^0)
1(16) + 3(4) +2
16+12+2
30
Diagrams
- Units
- The number of individual units
- Longs
- A collection of units. Number determined by base, or how many units fit into that particular long. If 6 units made up the long it would be a base six long.
- Flats
- A collection of longs. Number also determined by the base. If 6 longs could fit into the flat, then it would be a base 6 and hold 36 units.
- Any digit in a number may not be equal to or exceed the number of the base.
Working with bases
Subtraction
25 base seven - 15 base seven =10 base seven
34 base six - 15 base six = 15 Base six
- Convert one Long into Units to be subtracted
21 base four - 13 base four = 2 base four
- Subtract one long (21-13), then convert the other into four units to subtract the three, after which there will be one unit left, in addition to the one in 21
Addition
8 base nine + 13 base nine = 21 base nine
12 base six + 20 base six = 32 base six
232 base four + 101 base four = 333 base four