Drivers (causes)
Technology & communications
Transnational Corporations
States and Global governance
Ideology
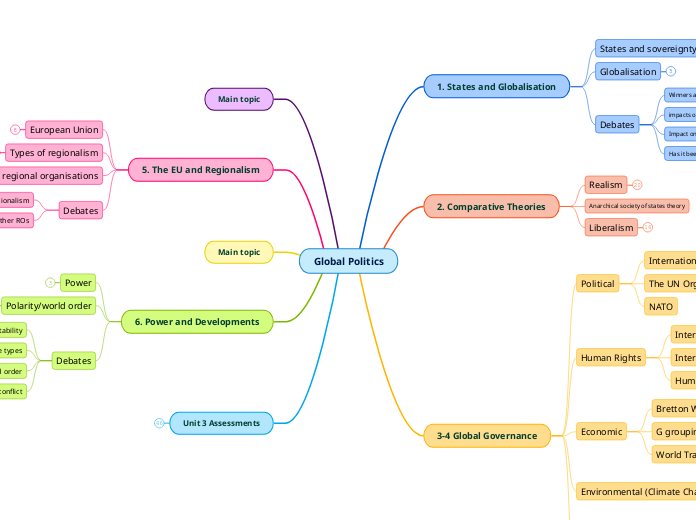
Global Politics
Unit 3 Assessments
30 mark debate questions
Synoptic
Use comparative theories if you can
Covers two or more topics
Comparative evaluation of two..eg.
forms of polarity
forms of governance
usually evaluation of
change over time
significance
Standard essay structure
main conclusion
3 analytical/evaluative sections
mini conclusion
against
for
intro - line of argument
Evaluate the view that
Choice of two out of three questions
12 mark comparative questions
Section B - comparative theories
Realist vs liberal view on e.g
conflict
world order
power
significance of states
human nature
Compulsory/no choice
Section A - comparative analysis
Compare two e.g.
states (power)
impacts
causes
processes
concepts
institutions (governance)
effectiveness
features
Choice of two questions
1 comparative theme in each paragraph
No intro or conclusion - no AO3 evaluation
Approx 1-1.5 pages
3 paragraph structure
6. Power and Developments
Likelihood of superpower conflict
Current world order
Impact of regime types
Polarity and stability
Polarity/world order
multipolarity
bipolarity
unipolarity
Power
State power rankings
Power classifications
Types of power
5. The EU and Regionalism
EU as a model for other ROs
Prospects for future regionalism
Other regional organisations
Arab League
African Union
NAFTA/USMCA
ASEAN
Types of regionalism
European Union
Global significance and prospects
Integration
Security
Enlargement
Development & structure
Main topic
3-4 Global Governance
Effectiveness of output
Climate change
Human rights
Poverty reduction
Conflict resolution
Institutions
Need for reform
Legitimacy
Impact of state power
Environmental (Climate Change)
Process
Summits
Conventions
UN bodies
Issues & perspectives
World Trade Organisation
G groupings
G20
G7
Bretton Woods System
World Bank Group
International Monetary Fund
Human Rights
Humanitarian intervention
International Courts & Tribunals
ECHR
International Criminal Court
Yugoslavia
Rwanda
Nuremburg
International HR law & UN HR bodies
Political
NATO
The UN Organs
International Court of Justice
Economic & Social Council
General Assembly
Security Council
International law and UN Charter
2. Comparative Theories
Liberalism
Locke
Mechanistic theory
Commonwealth & social contract
Rule of law
Rationalism & enlightened self interest
Neo
Fukuyama 'end of history'
liberal institutonalism
Keohane
interdependence liberalism
democratic peace theory
Kant 'perpetual peace'
Anarchical society of states theory
Realism
Links to core ideologies
Leviathan and order
Human nature
State of Nature
Neoclassical
Human nature & structure
Neo/Structural
Huntington 'clash of civilisations'
Anarchic state system
Offensive
Mearsheimer
Defensive
Waltz
Classical
Power/human nature
Morgenthau
Hobbes
Machiavelli
Thucydides
1. States and Globalisation
Debates
Has it been exaggerated?
Impact on state sovereignty
impacts on conflict, human right, poverty & environment
Winners and losers
Globalisation
Phases of development
Types and features
Political (Global Governance)
Cultural
Economic
States and sovereignty
Complex interdependence
The International State System