Horizontes historico-culturales de Mesoamerica
Type in the name of the multiple-perspectives text.
Example: Bridge to Terabithia by Katherine Paterson
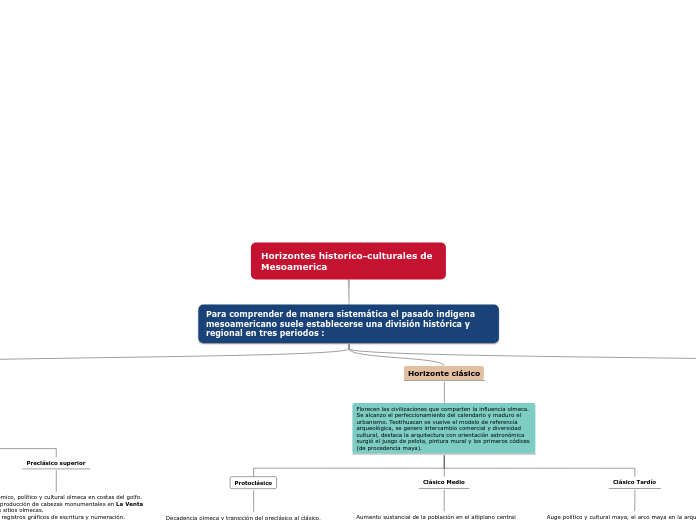
Para comprender de manera sistemática el pasado indígena mesoamericano suele establecerse una división histórica y regional en tres periodos :
Identify an important issue from the text that is being presented from different angles. Type it in.
Example: Jesse's drawing talent.
Horizonte posclásico
Decide on the fourth point of view
Type in the name of the last character whose perspective on the issue you are going to present.
Example: Leslie Burke, Jesse's new next-door neighbor, and best friend.
Auge de las tendencias migratorias, grupos chichimecas procedentes de Aridoamérica en el altiplano central además se fortalecen estados militares como los toltecas, purépechas en Michoacán, mixtecos en guerrero y Oaxaca . Etapa con mayor abundancia de códices en diferentes regiones, se considera al posclásico tardío como un horizonte histórico.
Point of view
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view. Try to follow a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: I can't get the poetry of the trees,' he said. She nodded. Don't worry,' she said. You will someday. He believed her.' (Paterson, 4. 24)
Posclásico superior
Fundación de México Tenochtitlan en un islote del valle de México, integración de la triple alianza entre Tenochtitlan, tlacopan y Texcoco. Expediciones españolas procedentes de cuba, se llegan a recorrer las costal del golfo de México. Hernán Cortez realiza la conquista de México entre 1519 y 1521
Posclasico inferior
How is the viewpoint introduced in the story?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
Reorganización política, social, militar y territorial, predominio tolteca, decadencia maya y nuevos núcleos de poblamiento además de la decadencia tolteca
Horizonte clásico
Whose character does the third point of view belong to?
Type in his/her name.
Example: Mr. Aarons, Jesse's father.
Florecen las civilizaciones que comparten la influencia olmeca. Se alcanzo el perfeccionamiento del calendario y maduro el urbanismo. Teotihuacan se vuelve el modelo de referencia arqueológica, se genero intercambio comercial y diversidad cultural, destaca la arquitectura con orientación astronómica surgió el juego de pelota, pintura mural y los primeros códices (de procedencia maya).
What does the character think, say or do that suggests their perspective on the issue?
Type in a quote and try to maintain the citation format.
Example: 'He would like to show his drawings to his dad, but he didn't dare. (...) He'd thought his dad would be pleased. He wasn't. What are they teaching in that damn school? he had asked.' (Paterson, 2.8)
Clásico Tardío
Auge político y cultural maya, el arco maya en la arquitectura, sistema vigesimal maya, perfección del calendario. decae Teotihuacán y se incrementan las fricciones fronterizas en diversas regiones y tendencias migratorias.
Clásico Medio
Aumento sustancial de la población en el altiplano central urbanismo auge arquitectónico monumental y habitacional.
Protoclásico
What kind of narration introduces the viewpoint?
Choose an answer:
First person point of view - using the personal pronouns 'I' or 'we'Second person point of view - using the personal pronoun 'you'Third person point of view - using the third-person pronouns 'he', 'she' and 'they'Omniscient point of view - an all-seeing observer tells the story
Decadencia olmeca y transición del preclásico al clásico, primeros vestigios arquitectónicos en Teotihuacán.
Horizonte preclásico
Decide on the first point of view you are going to present.
Type in the name of the character (it can either be the main character or one of the supporting characters) whose point of view belongs to.
Example: Jesse Oliver Aarons, Jr., the main character of the novel, a fifth-grader living in a rural Southern area.
Dominio de la agricultura propicia una vida sedentaria en aldeas en sitios fértiles. El culto al jaguar y al viento como primeras manifestaciones religiosas además que surge la escritura, numeración y el calendario mesoamericano.
Type in a relevant quote that highlights the character's point of view towards
Para comprender de manera sistemática el pasado indígena mesoamericano suele establecerse una división histórica y regional en tres periodos :.
Try following a citation format: author's name, chapter, and page.
Example: 'Jesse drew the way some people drank whiskey. (...) Lord, he loved to draw. (...) When he was in first grade, he told his father that he wanted to be an artist when he grew up.' (Paterson, 2. 7)
Preclásico superior
Auge económico, político y cultural olmeca en costas del golfo. Abundante producción de cabezas monumentales en La Venta y diferentes sitios olmecas. Estelas con registros gráficos de escritura y numeración. Expansión e influencia olmeca en otras regiones de Mesoamérica
Preclásico medio
Incremento de la población y desarrollo de la arquitectura. Desenrollamiento de la escultura.
Preclásico inferior
Poblamiento de las costas del golfo de México y el desarrollo agrícola. Abundancia de figuras femeninas de barro.