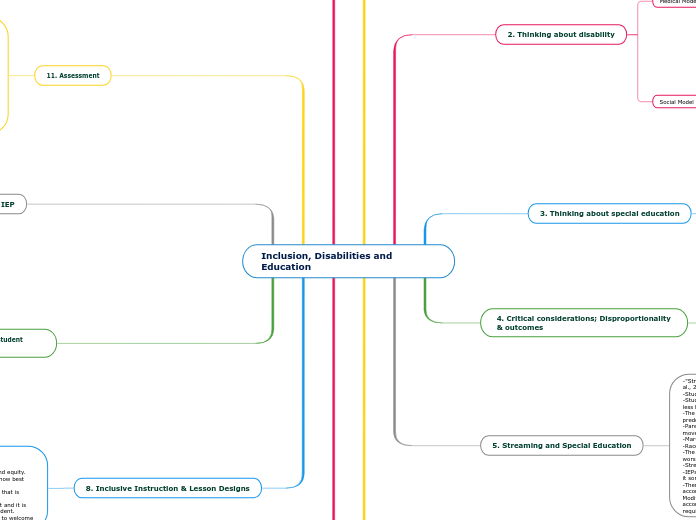
Inclusion, Disabilities and Education
Type in the title of your course.
7. Inclusive Design - Strategies ,Tips and Tricks
Group work contributes to inclusion.
-All students need a chance to participate.
-Select positive disability text.
-Be Culturally Responsive and integrate stories of persons with disabilities and challenge charity and medicalized view.
-Include students in meeting with families.
8. Inclusive Instruction & Lesson Designs
Differentiation
-This requires preparation, flexibility and choices.
-Identify students interest.
-The environment must support accommodation and equity.
-Educators need to understand their student and how best they learn.
-This will help them to collaborate and build a plan that is suitable for the student.
-Collaboration is an important tool for development and it is important that this behavior is modeled for the student.
-Different perspectives are a bonus and it will help to welcome different ways of learning.
9. Student perspectives/incorporating student voice
-Students with disabilities are often dehumanized.
-They are kept in the dark about their learning disabilities.
-This act leaves them without explanation for the way that they are feeling and it becomes internalized that they are not smart.
-Student demand better accommodations.
-Students with disabilities want to be to included in decisions that concern them, they want a seat at the table.
-They also demand an inclusive environment.
-They want to be protected from bullying and harsh language.
-Better co-ordination is needed between families, school and other community partners. (PACY, 2016)
10. Developing An IEP
-It does not have everything that will be taught to the student.
-A list of teaching strategies used in regular classroom.
-A record of all learning expectations.
-A daily lesson plan.
AN IEP can accommodate or modify to help students to attain their academic goals.
Modification situates students further away from academic achievements.
Accommodation removes and prevents barriers from impeding the students ability to participate.
Benefits of an IEP to students
-It creates opportunity and fit students academic need.
-It allows students and educator to have structure.
-It is an individual action plan.
-It is a collaborative effort between parents, educators and community partners.(Lesh, 2020)
11. Assessment
Assessment
-FOR learning (pretest).
-As learning (self and peer assessment)
-OF learning (summative, final project, paper)
Seven principles of assessment
All students must be supported, including those with special needs, language learners, Indigenous and metis.
-Teacher should be fair, transparent and equitable.
-Learning goals are not arbitrary and relate to the curriculum, interest and need of the student.
-Ongoing open and clear communications to parents and students.
-Students being given multiple opportunities to show their learning.
-Clear, timely and meaningful descriptive feedback.
-Help students to develop self- assessment skill so that they can set goal and plan next steps.
Educators bring some bias to this equation
-We all have an idea of what success looks like and it is Eurocentric ableism. We must change our paradigm to include a more diverse swath of the school population.
-Learning Skills are used to determine stream and in specialized programs they are valued over academics.
-Teachers must be vigilante of their own implicit biases during assessment.
12. Working with support staff
The evaluation must go hand-in-hand with course goals in order to achieve them and also help students to improve their skills.
Also, assignments and homework need to reflect and help achieve course goals.
Who is in the classroom?
-There are several professionals who maybe a part of the classroom.
-They are education assistance, child and youth workers, social workers and more.
-EAs support the teacher to carry out education plan.
-Work with students to achieve their academic goals.
-Assist students with disabilities.
-EAs support student both in an academic and personal capacity.
CYW
-work with students who demonstrate emotional and behavioral challenges.
-Work with families and students.
Social Workers
are liaisons between families, school and community partners.
Decide if you want the assignments completed during the year to represent 1/3 of the final grade.
Path to Success
-There must be communication and collaboration among all professional in the classroom.
-Weekly meeting to debrief and set the future agender.
-Have a system to report incidences.
-Practice inclusivity among staff.
6. What is inclusive education
What inclusive education is not?
-It is not assimilation, nor is it a way to make everyone the same.
-Its goal
What is inclusive education?
-An inclusive classroom is a space where all students are welcomed.
-Environment is modified to fit the student's need and not vice vice versa.
-Prioritizes the right to participate.
-It rejects deficit thinking and do not practice segregation nor group students according to their ability.
-It is a space where diversity is celebrated and students with disability can feel a sense of pride.
What can educators do
-Value difference and celebrate diversity.
-Practice student‐centred pedagogy over curriculum‐centred pedagogy.
-Ensure accessibility to curriculum.
-Provide support within the classroom.
-Promote students sense of belonging.
-Support the self‐organization of students with disabilities.
-Set goals and organize in collaboration with community, parents, educators, local government and non‐government agencies. (Parekh & Underwood, 2015)
5. Streaming and Special Education
-"Streaming is a form of institutional violence". (Clanfield et al., 2014, p. 261)
-Students are grouped according to their perceived abilities.
-Students who are streamed away from the academic path is less likely to go to university.
-The academic trajectory for students of color is predetermined to the applied and non academic path.
-Parents are given false information that students can freely move from one path to another.
-Marginalized students are disproportionally streamed.
-Race and class are major factors in streaming.
-The intersectionality of race and gender makes the outcome worse.
-Streaming is a generational problem.
-IEPs are used to help students meet their academic goals but it sometimes lack current data.
-There is a significant difference between modification and accommodation.
Modification changes the student's academic trajectory, while accommodation provide a path for student fulfil curriculum requirements. (San vincente, 2016)
4. Critical considerations; Disproportionality & outcomes
Arrange the topics in a logical order.
Discuss how and why you have organized the material in a particular way.
This will help students to see the connections between topics.
-Race, gender and class are determinants to a student's academic path and future.
-Minority and poor students are over-represented in special education programs and under-represented in college admissions.
-Euro-centric ideals are the standard within our educational system and if you do not fit that mold then you are labeled and treated as other.
-The above is an historical issue that we continue to grapple with.
-Oftentimes the onus is on students who are affected by this system to overcome all these insurmountable obstacles through individualism and merit.
- Chronological - you can organize the topics according to a theme or storyline.
- Topical order - involves taking the topic of your speech and dividing it into several subtopics. The subtopics are related to the topic they branch out from.
- Survey-oriented - this type of course structure is briefly treating the main topics of a broad field of knowledge.
- A process-oriented syllabus focuses on the skills and processes involved in learning.
ChronologicalTopicalSurvey-orientedProcess-oriented
3. Thinking about special education
-The focus of special education is to help students with disabilities learn in an inclusive classroom.
-The guideline for special education varies from board to board; there are no standardized rules.
-There are several strategies that can be used t help students, assistive technology, accommodations, modification and paraprofessional.
-If there is a need for a IEP, it will be tailored to the student's need and it is a legally binding document.
-IPRC- two thing are identified during this meeting, identification and placement.
2. Thinking about disability
Select the major topics and determine the order in which you will teach them.
Social Model
You can change your initial list of topics. You can add more material or interesting facts on the subject if your time allows it.
You can even add to the list some movies that are worth watching and will help you to achieve your goal.
-It is societal attitude and polies that constructs barriers
-Unlike the medical model of disability, the environment is the focus (Baglieri, 2017).
-This is a comprehensive look on the political, social and physical environment and how persons with disabilities are affect by such discourse.
Medical Model
Select the main topics to be covered. To obtain an initial list of course topics, search in current textbooks or in the current literature.
-Persons with disability is an object to be diagnosed and fixed.
-It is the framework of this person's life and it boxes them in, therefore, they are not seen as whole.
-It values the community partner above the person because they are the expert.
-The person with disability must comply because of the expertise.
-There is an importance placed on diagnosis and care, in an ongoing effort to mend the person.
-It is mainly about taking a path that leads to 'normal'. (Baglieri, 2017)
-The way that society views disability is a cultural.
-There are two lens through which we view disability, the medical and social model.
-The cultural meaning regarding both model is not static, it changes when society changes.
1. Teaching and learning in a pandemic
Determine the goals of the course.
Having these course goals in mind will then help you make decisions about which content to include and what kind of assignments and exams are appropriate.
Consider the following questions:
- What you want your students to remember from your course?
- What skills should students gain in this course?
- How does this course relate to other courses in the discipline?
-Classrooms must be inclusive.
-Families and children with disabilities face discriminations constantly.
-Persons with disabilities are often dehumanized and are thought of as acceptable causality (Wong, 2020).
-Disparities with our health and education system have been exposed especially during the covid19 pandemic.
-Teachers must be committed to inclusive education.
-Covid19 has made accommodations possible.