Dipole Dipole
organic compounds with dipole dipole forces are most soluble
polar solvents
the positive ends and the negative ends of the moleucles interact with each other
they are highly soluble in water. (water is a polar solvent)
polar molecules. when the positive end of one polar molecule interacts with the negative end of another polar molecule
higher boiling/melting point then london dispersion forces but lower then hydrogen bonds (Langdon, n.d., p. 2.4)
interactions between dipoles on neighbouring molecules
London Dispersion forces
olive oil
Subtopic
poorly soluble in water
difficult to overcome the hydrogen bonds in water molecules
low boiling/melting point (Reusch, 2020, p. 2.11)
weakest forces
the instantaneous forces are formed through random motion of electrons
organic compounds with only london dispersion forces are most soluble in
occurs between all molescules
Hydrogen bonds
non-polar solvents
highly soluble in water (Langdon, n.d., p. 2.4)
high boiling/melting point (Reusch, 2020, p. 2.11)
when reacting with a highly electronegative atom ( between H and F, N, or O) via polar covalent bond
strongest forces
Intermolecular forces
into 3 types
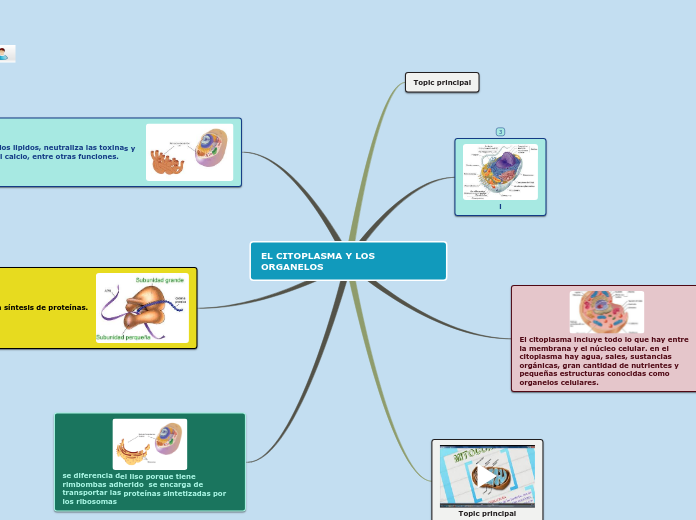
lipids
hydrogen bonds
semi-fluid at rtp
phospholipids
unsaturated fats
vegtable oil
weaker London dispersion forces
liquid at rtp
saturated fats
stronger london dispersion forces (Molecular Shape and Functionality, n.d., p. 5)
solid at rtp