RULE OF 72
72 / Interest rate = # of years to double money
COMPUND INTEREST
Present $ x Interest Rate x Time = Interest
COMPNENTS OF
A BUDGET
REVENUE
Income after taxes (Net)
EXPENSES
Fixed monthly (mortgage, cable, internet)
Variable (gas, groceries, meals, entertainment)
Occasional
Characteristics
Opportunity Obsession
Find and fix problem
Self Reliant
Control their results
Believes in themselves
Creative
Inventive and innovative
(looks for new ways of doing things)
Confidence
Important to have that feeling of
certainty/trust in yourself in order to do well
Motivation to Excel
Doing things for themselves
NOT for power/status
Commitment
Conquer, drive, passion
Leadership
Good management abilities
Teamwork
Risk-Takers
Weighs risks before jumping in
(BOTH good and bad risks)
Introduction to Business
(BBI101)
Innovation
Improve on an existing invention
Invention
Creating a product from scratch
Setting up business/businesses.
- Taking calculated risks
Elevator Pitch
Brief, persuasive speech used to spark interest to what you're doing
20-30 seconds
Steps
Engage: Get customers involved, attract attention
Uniqueness: What makes project different from others?
what's unique?
What do you do? Describe what project is about
Loscus of Control
Refers to extent to which people believe
they have power over events in
their lives.
External: Passive
"things happen to me"
Internal: Active
'I can make this happen"
Roles + Contribution
Act
QUICK
Don't wait for others to figure out the problem
Solve
Find ways to fix problem
Must be able to get customers to buy
for their needs & wants
Recognize
Look for problem
Problem:
Needs & wants expectations not being met
What motivates entrepreneurs?
Sense of accomplishments
Carry on family business
Being challenged
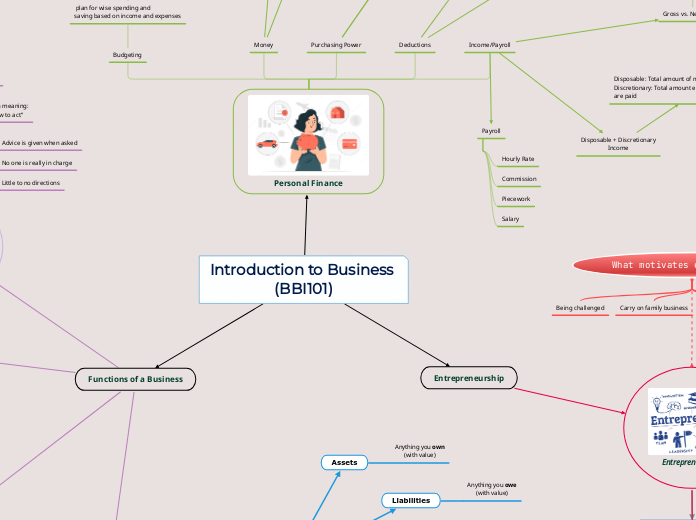
Personal Finance
Income/Payroll
Disposable + Discretionary
Income
Disposable: Total amount of money earned after taxes
Discretionary: Total amount earned after all basic necessities are paid
Payroll
Salary
Piecework
Commission
Hourly Rate
Gross vs. Net Income
Gross: $ a person earns BEFORE taxes
Net: $ a person owns AFTER taxes
Deductions
Taxes
eg. EI, CPP
Money is used to pay for:
Police, Health Care, Jails, Education, Roads, Welfare/Social Assistance.
Mandatory: By law, your employer takes deductions off pay cheque and send to government
Voluntary: Optional deductions taken off your pay
Income - Deductions = Net Income
Purchasing Power
The more $ you have, the more
you're able to purchase
items in markets in exchange
Spend
Save
Invest
Donate
Gamble
PURCHASE DECISIONS
Money available
Costs
Buyer Behaviour
Quality
Comparison + Product info
Service
Warranties/Guarantees
Money
Medium that can be
exchanged for
goods and services
Paper
Notes
Coins
Cheques
When do we still use?
Income payment
Large Payments
Government Payments
Gifts
Components
Name
Address
Name to whom it's sent to
Description
Cheque #
$ amount (standard)
$ amount (words)
Signature
Budgeting
plan for wise spending and
saving based on income and expenses
YOU CAN:
Organize and control your financial resources
Set and realize goals
1. Calculate what you own
2. Calculate what you earn (NI)
3. Calculate what you owe
4. Calculate what you spend
Daily, weekly, monthly
Functions of a Business
Marketing
Marketing Mix
4 P's, 2 C's
Competition
Direct
Indirect
Consumer
Target Market
Promotion
Informs consumers about a product
and encourages them to buy it.
Publicity
Public Relations
Sales promotion
Telemarketing
Personal selling
Place
Price
Often determined by
quantity demand
Product
Packaging
aka. Silent Salesperson
Jingles
Slogan
(7 words or less)
Logo
Trademark
Labelling
Advertising
AIDA (Selling Formula
- Attention
- Interest
- Desire
- Action
Goals of Advertising (RIP)
- Remind
- Inform
-Persuade
Accounting
Income Statement (3 $ Signs)
R - E = NI
Net Income/Loss
aka. Profit/Loss
Expenses
Money you spent for business
Revenue
Money that you earned within business
Balance Sheet (4 $ Signs)
A = L+OE
Owner's Equity
Net Worth
"Leftover" (Capital)
Liabilities
Anything you owe
(with value)
Assets
Anything you own
(with value)
Production
Production Process
Grading
Quality Control
Process
Purchase
Productivity:
The effectiveness of productive effort, as measured in terms of the rate of output per unit of input. Increasing productivity leads to increased profits for an organization.
Inventory systems
Invest in Technology
Capital Investment
Training
The action of making/manufacturing
from components
Entrepreneurship
Human Resources/Labour
Capital
Land
Leadership & H.R.
Roles of Management
Controlling
Ensuring company goals are met
Organizing
Structure of event
Specific tasks
Procedures
Planning
Starts with research
Maslow's Motivators
Growth Needs
Work to gain experience to get promotions
Challenge people
Offer support
Existence Needs
Work for money, nothing else
Pay people enough
Set goals
Relatedness Needs
Interacting with people, have personal challenge
and sense of achievement
Show respect
Communication
POSITIVE VS. NEGATIVE LEADERS
Negative
Are dominant, act superior
with people
eg. Penalties
No pay
Assigning tasks that are unpleasant
Positive
Use rewards to motivate employees
Independent
Raises/Bonuses
Acknowledgement
Types of Leadership
Laissez-Faire
French meaning:
“Allow to act”
Little to no directions
No one is really in charge
Advice is given when asked
Democratic
Leader has final say
Supports teamwork
All members involved
Autocratic
Not open to new ideas
Boss tells what to do