作者:Juan Enrico Miguel Sandoy 7 年以前
265
Juan Enrico Miguel Sandoy
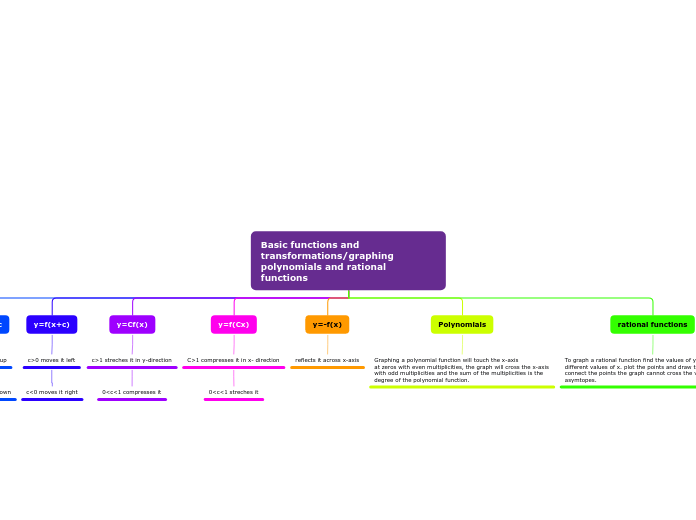
Polynomial functions include quadratic, cubic, quartic, and higher-degree equations involving non-negative integer powers of x. The multiplicity of a root refers to how many times a particular number is a zero of the polynomial.