Literature
Topic principal
Critical Viewpoint
ETHNIC VIEWPOINT
Consider how ethnic groups are portrayed within the work.
FEMINIST VIEWPOINT
Consider how the work portrays women and approaches gender roles.
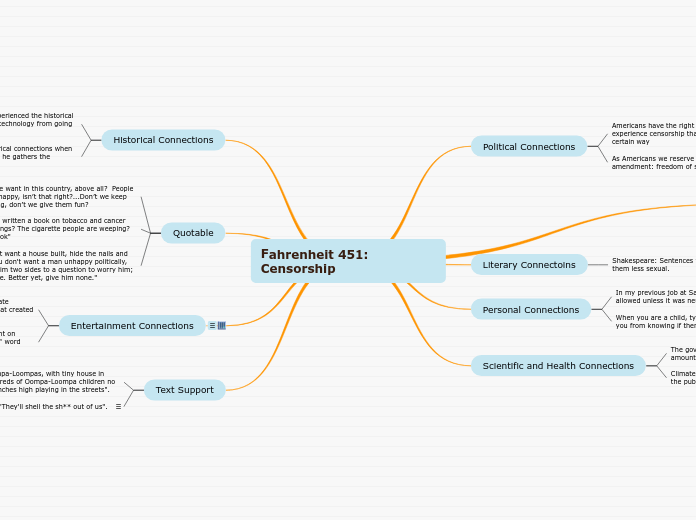
POLITICAL VIEWPOINT
Consider how political systems and politics are portrayed in the work.
Literary Criticism
PARADIGMS
Formalism
Marxism
Feminism
Psychoanalytic
Cultural Criticism
Structuralism
Post-structuralism
Archetypal
Examples of Archetypes
Characters:
*Scapegoat
*Hero/Villian
*Outcast
*Temptress
*Mother/Father
*Mentor
Feminist Criticism
*Feminist criticism grew out of the women’s movement that followed World War II.
*Look for systems of containment; for evidence of repression, oppression, suppression, subversion, & rebellion.
Structuralism
*Meaning resides in the structure of language, not in art nor in the reader’s mind.
*Scientific approach to literary analysis:
*Structure of language as a logical sign system determines meaning
Formalism
*Form, organization, and structure
*Word choice and language
*Multiple meanings
To Analyze, Study, & Evaluate Works Of Literature.
Relationship Between Authors, Readers, & Texts.
Evaluation Of Literary Works
Mimesis
ARISTOTLE
Logos
Phatos
Ethos
STEMMING
*Multiple meanings
*Word choice and language
*Form, organization, and structure
FORMALISM
Imitation Of Life In Art & Literature
A Source of Knowledge, Wisdom, Purgation, Prophecy
Author's Inner Being
Defined thesis; it is PERSUASIVE
Does not provide a summary.
Explains a literary work in a formal essay.
Literary Analysis
QUALITY
The resources of language and meaning are used to reveal the depth and complexity.
Literature has to use all of its resources well.
COMPLEXITY
Elements:thought, feeling, sensation, memory, imagination, significant symbols
Environment, character, situation.
Being made up by interacting factors.
LITERARY ELEMENTS
DICTION
Focus on the words of the work.
CONNOTATION
Analyze the figures of speech and sound effects of the work.
CONFLICT
THEME
FORM/STYLE
*Poetry
*Fiction
*Drama
ATTITUDE
IMAGES
Character Types
Static Characters
Are characters who do not change throughout the story.
Dynamic Characters
Are characters who go through a significant change in the story, The protagonist.
Round Characters
Are multi-dimensional and are usually the protagonist.
Flat Characters
These characters are usually minor characters.
DEPTH
We experience life with complexity.
Our lives hold symbolic and historical meaning.
Authors seek to define some of the forces and
feelings which give importance to our being.
LITERARY TECHNIQUES
Irony: It is use of the words in such a way in which the intended
meaning is completely opposite to their literal meaning.
Personification: It gives a thing, an idea or an animal human
qualities.
Allegory: It is a literary technique in which an abstract idea is
given form of characters, actions or events
Alliteration: It refers to the same consonant sounds in words
coming together.
Imagery: It is use of figurative language to create
visual representations of actions, objects and ideas in our mind.
Simile & Metaphor: Both compare two distinct objects and draws
similarity between them.
Hyperbole: It is deliberate exaggeration of actions and ideas
for the sake of emphasis
Literary Genres
TYPE OF LITERATURE, MUSIC, ART, TV SHOW, MOVIE, VIDEO GAME, ETC.
Historical Fiction
Fantasy
Science Fiction
Mystery
Horror
Thriller
Survival/Adventure
Folk Tale
Legend
Biography
Memoir/Autobiography
Drama
Humor
Depict
Genre, Text or Discourse
Knowledge & Clarifiying Emotions
External & Internal Realities
Interpretation
INVOLVES
Exegesis
Nature Of Reading and Theory and Criticism
Personal Response, Appreciation, Evaluation etc.