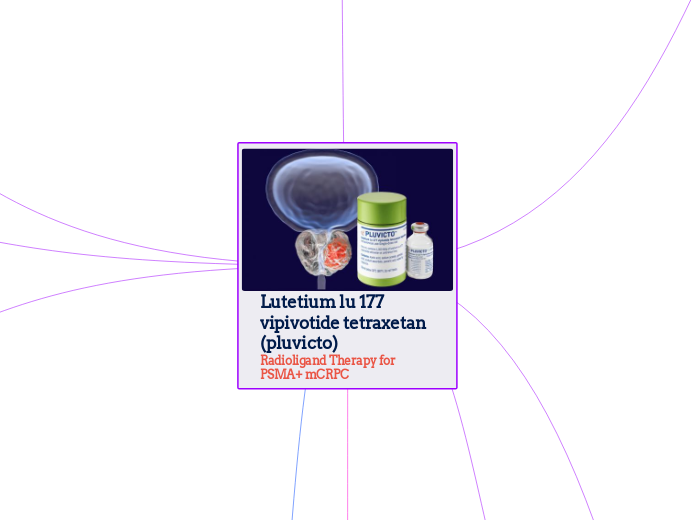
Lutetium lu 177 vipivotide tetraxetan (pluvicto) Radioligand Therapy for PSMA+ mCRPC
Vison Trial
Adverse effects
Renal toxicity
0.9% - ↑ creatinine
3% - Grade 3 or 4 acute kidney injury.
Myleosupression
Fatal events (n=5)
1.1% grade ≥3 pancytopenia occurred (including 2 fatal events)
15% grade 3 /4 ↓ hemoglobin ↓ 9% platelets ↓ 7% leukocytes ↓ 4.5% neutrophils
Results
Secondary end point
Significant increase in Overall Response Rate (ORR)
PSA Decline 46% vs VS 7% 46% of patients who received Pluvicto (BSOC) PSA decline ≥ 50% VS 7%B SOC alone
Primary end point
Median Overall Survival 15.3 months-11. 3 months
Radiographic Free Survival 8.7 months- 3.4 months
Trial Characteristics
Prospective open labelled trial
FDA Approval
Pharmacovigilance
ongoing
Approval in the EU
13 October 2022
USA
2nd of March 2022
Following VISION trial
Manufacturing/ handling
Storage/ Handling
Disposal
Consult the product batch release certificate to identify the source of stable isotopes used- appropriate management for different types of isotopes
In accordance with local radiation safety federal laws.
Storage
Store below 30 do not freeze
Shelf life
120 hours (5 days)
manufacturing
Supply
Struggled to produce/ source enough radioactive material to meet demand
Manufacturing halted last May to sort out supply issues- resumed
2 different stable isotopes: Leutium 177- PSMA 176 + ligand
Complex to make
Pharmacoeconomics
Quality of life
Pluvicto: OS =15.3 months (4 months > then BSOC)
Estimated 38% reduction in risk of death
90% chance of developing bone metastasis (fractures, spinal chord compression)
No therapeutic options remaining
Safety Information
Potential adverse/ adverse drug events
Most Frequent
Potential averse effects/ clinically relevant
Severe renal toxicity
Embryo-fetal toxicity
Life threatening myleosupression
Infertility
Contributes to long-term cumulative radiation exposure.
Minimise close contacts
Minimise effects of radiation by :
Administration precautions
Principles of ALRA (as low as reasonably achievable).
Pharmacokinetics
Clearance
Exposure of drug to kidneys increases with decreasing creatinine clearance.
No dose adjustment rec-ommeded - kidney imparimeny- risk of toxicity
Effects of more severe kidney impairment or end stage kidney disease has not been investigated.
Primaly excreted via the kidneys
Metabolism
Substrates - not a substrate of CYP450 enzymes or of transporters OAT1,OAT3, OCT2.
60-70% bound to human plasma proteins.
Distribution
Within 2.5hr administration - Gastrointestinal tract, liver, lungs, kidneys, heart wall, bone marrow, salivary glands.
Volume of distribution : mean = 123 L
Absorbtion
After Iv admin- mean blood concentration 6.58ng/mL
Whole body and organ radiation dosimetry collected in a subgroup of patients the phase 3 vision trial. n=29
Radiation absorbed doses [mean calculated absorbed dose for 6 x 7.4 GBq (44.4 GBq cumulative activity)
The 6-cycle cumulative estimated absorbed dose in the blood-based red marrow was 1.5 Gy.
Maximum penetration of lutetium-177 in tissue is ≈ 2 mm (mean penetration is 0.67mm)
Organs with highest radiation absorbed: Lacriminal glands, salivary glands , large intestine (left colon, rectum, right colon,kidneys, urinary bladder wall).
Dosage
Supplied: 30 mL single dose vial. Pluvicto solution for injection contains : 7.4 GBq (200 mCi) of radioactivity (at time of use). Slow IV injection (1-10 mins)/ infusion
Administered every 6 weeks for up to 6 treatments.
Administered by a healthcare professional, certified in radio pharmacotherapy.
Blood tests preformed pre and during treatment to monitor PSMA levels.
Do
Pharmacodynamics
Mechanism of Action
Targeted Radioligand therapy
Targeted RLT offers the possibility to treat prostate cancer lesions in a specific and tumour selective manor by exploiting the cell surface proteins mainly expressed on maligant cells.
PSMA-617 (precursor molecule)
Therapeutic radiation can be delivered via PSMA while minimising radiation related side effects. PSMA -targeted RLT uses a radiolabelled small molecule ligand (PSMA617) that binds with high affinity to PSMA, resulting in internalisation and retention within the targeted PC cell.
PSMA-617 complexed with radionucleotide Lu-177
Intra tumoral half life
60/160 hours
Maximal tissue penetration
2mm
Path length of B particles
medium length B emitter
shorter B length- better irradiation for small tumours
direct energy to tumour than surrounding tissue
Physical 1/2 life
6.64 days
+ high intratumoral retention
reduces dosing frequency
Target
PSMA
PSMA is a transmembrane glycoprotein involved in various cellular functions, such as cellular uptake of folate, cell migration, and cell survival.
While PSMA is expressed at low levels in normal prostate epithelium, it is overexpressed (up to 1000 times higher) in 90–95% of prostate cancers. In contrast to benign prostatic epithelium where PSMA resides in the cytoplasm, PSMA is in the luminal epithelium of prostatic ducts in prostate cancers and presents a large extracellular binding domain .
PSMA expression is positively correlated with more aggressive disease, including high PSA, high Gleason scores, and early recurrence. The highest levels of PSMA expression are found in metastatic and castrate-resistant disease
Due to its overexpression on the surface of PC cells, PSMA remains a useful protein target for targeted diagnostic processes and radionuclide therapy in PC
>80% of patients with prostate cancer express PSMA
Therapeutic Indications/ eligibility
Androgen deprivation therapy, in adults previously treated with androgen receptor pathway inhibitors and taxes.
Administered with androgen deprivation therapy
Androgen receptor pathway inhibitors
Taxanes
PET scan performed to check PSMA+ for Pluvicto eligibility
Prostate Cancer
Pathophysiology -mCRPC
Metastatic Prostate Cancer (mPC)
Androgen Depletion Therapy is continued
ADT highly effective- elicits a PSA response
10/20% of patients become castration resistant within 5 years
Castration Resistant Prostate Cancer Therapeutics
>50% die within 3 years with historical standard therapies
NCCN,ESMO,APCCC
None have been proven to prolong survival
No proper sequence for delivery
Tax and based chemotherapy
Chemotherapy side effect profile
Limited options failure of chemotherapy
l
5 year survival = 30%
90% of patients with mCRPC develop bone metastasis
Localised Prostate Cancer
Androgen Depletion Therapy (ADT)
Radiological therapy
Surgical
Epidemiology
2nd leading cause of cancer related death among men in the USA. 3rd leading cause in Europe.
2nd most common cause of cancer in men globally