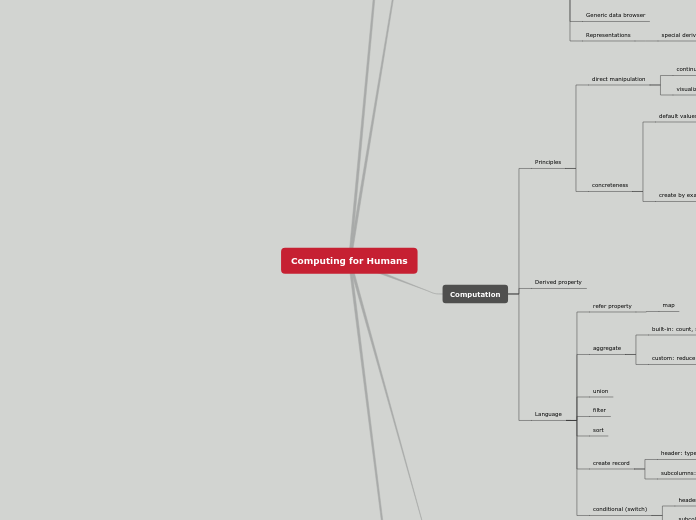
Whole Numbers
Multiplying
Exponents
Repeated multiplying of the same number may be reduced to a superscript of the amount of times the number appears in the equation. This is read, "to the [#]th power."
n x n x n = n^3
Cubed
Multiplying a number by itself three times.
n x n x n
Squared
Multiplying a number by itself once.
n x n
Identity Property of One
Any number multiplied by one will result in the original number.
n x 1 = n
Multiplication Property of Zero
Any number multiplied by zero results in zero.
n x 0 = 0
Changing the grouping of factors does not change the product.
(ab)c = a(bc)
Changing the order of factors does not change the product.
ab = ba
Subtracting
Because it represents repeated addition, multiplication may be distributed over subtraction separated by parentheses.
3(4 - 3) = (4 - 3) + (4 - 3) + (4 - 3)
Therefor,
a(b - c) = ab - ac
Altering the order of numbers will yield different results.
a - b =/= b - a
Adding
Distributive Property
Because it represents repeated addition, multiplication may be distributed over other addition separated by parentheses.
3(2 + 3) = (2 + 3) + (2 + 3) + (2 + 3)
Therefor,
a(b + c) = ab + ac
Associative Property
Added numbers may be grouped in any way with the same result.
(a + b) + c = a + (b + c)
Identity Property of Zero
Any number added to zero will always result in the original number.
a + 0 = a
Commutative Property
Numbers may be added in any order with the same result.
a + b = b + a
Terms
Like Terms
Combining Like Terms
Variable Term
Constant Term
Order of Operations
4. Add & Subtract
After all other operations have been completed, addition and subtraction equally share the lowermost priority; they must be fulfilled from left to right.
3. Multiply and Divide
After parentheses and exponents have been fulfilled, multiplication and division equally share the next priority; they must be fulfilled from left to right.
2. Exponents
Numbers with exponents must be multiplied before they may be used for other operations.
1. Parentheses
Operations contained between the symbols ( and ) must supercede other operations.
Dividing
Not Distributive
Remainder
A remainder occurs when whole numbers do not divide evenly, and is signified with an R.
13/4 = 3R1
Dividing by Zero
Zero may be divided by any non-zero number, and will always result in zero.
0/n = 0
No number may be divided by zero; the result is undefined.
n/0 = ???
Dividing by One
Any non-zero number divided by itself is one.
n/n = 1
Any number divided by one remains unchanged.
n/1 = n
Not Commutative
Altering the order of numbers will yield different results.
a/b =/= b/a