作者:roslina mustapha 12 年以前
495
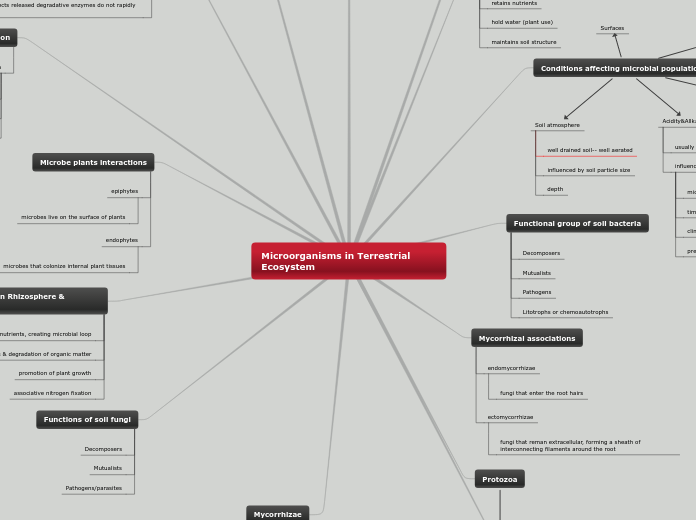
Soil Habitat
The presence and activities of microorganisms, particularly bacteria and fungi, play a crucial role in terrestrial ecosystems. These microbes are essential in the conversion of ammonium and nitrate into biomass, thereby stimulating soil population growth.