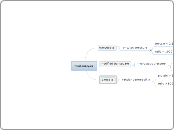
BIG IDEA I: BIOSPHERE
Ecosystem- such as the tundra
Communities- all biotic components in an area
Population- made up of plants, animals, and microorganisms
Organisms- such as polar bears in the tundra
Organ systems: such as the repitory system in the polar bear
organs- heart
tissue
cells- heart cell
organelles- lysosomes
molecules
BIG IDEA II: Chloroplasts
Calvin Cycle (no light)
CO2 fixed into G3P---> to carbohydrate
light reactions (uses light)
light strikes pigment molecule in PSII ; excites e- till it reaches the primary electron acceptor; makes NADPH & ATP
BIG IDEA III: Meiosis
Recessive
compared to dominant traits- do not have as much of an impact on expressed genes
Genotype
an organisms full hereditary information rvrn though not expressed always
Dominant
have a large impact on expressed gene
Phenotyes
organisms actual observed properties
BIG IDEA II: CELLULAR RESPIRATION
Oxidative Phosphorylation
ETC and cheiosmosis (inner mitochondrial membrane)
26 or 28 ATP
Subtrate Level Phosphorylation
Kreb's Cycle (2 cycle) matrix
1 FADH2
1 ATP
2 NADH+
3 NADH+
2 CO2
Glycolysis
Payoff
2 Pyruvate
4 ATP formed
Investment
2 ATP used
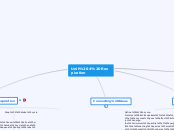
BIG IDEA I: Hydrogen Bonding
Expansion with freezing:
H bonds hard to break in crystal lattice formed by ice
Water is a very influential and versatile substance necessary to the life on earth. Therefore, it would have been placed at the top of the concept map since it relates to all the big ides in some form or fashion
Ability to Moderate Temperate
-
heat of vaporization
specific heat: amount of heat needed to raise one gram of a substance by 1 degree C
Cohesive Behavior
surface tension- responsible for dome shape
adhesive vs. cohesive
BIG IDEA III: Replication
Eukaryotes
replication occurs in the nucleus
Enzyme
DNA ligase
DNA Poly I & II
primase- synthesizes an RNA primer a 5' of leading strand and of each Okazaki fragment of lagging strand
topioisomerase- relieves the unwinding of the double helix
SSB- keeps this unwound
helicase- unwinds double helix at replication forks
Antiparallel
complementary base pairing
Prokaryotes
occurs in tht cytoplasm
Floating topic
BIG IDEA I: SRP
Polypetide not fully formed; attached to ribosome
SRP attaches to the signal petide chain
SRP leads the not fully formed peptide to the attached ribosome on the ER
Once there, the peptide chain continues to synthesize into the ER lumen; peptidase cuts off the synthsized chain
After being modified in the ER, vessicles travel on microtubules bringing the polypeptide chain to the Golgi for further modification
Once in the Golgi the protein can go four places
lysosomes
plasma membrane for secretion
back to the ER