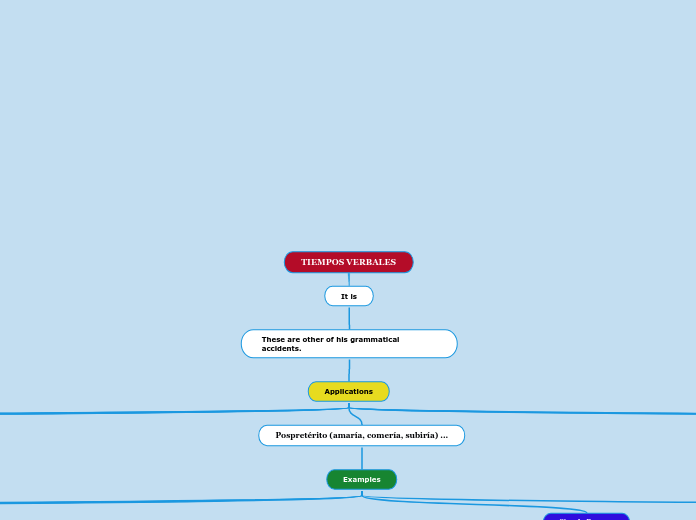
TIEMPOS VERBALES
It is
These are other of his grammatical accidents.
Applications
Antefuturo (habré amado, habré comido, habré subido)
Antepretérito (hube amado, hube comido, hube subido) ...
Antepresente (he amado, he comido, he subido) ...
Pospretérito (amaría, comería, subiría) ...
Examples
Futuro Perfecto (Future Perfect) I will have danced
Simple Present
Present tense that is used to talk about general facts or truths
Do/Does
The verb to do or does is used as an auxiliary to ask questions with present and past simple verbs, except if the verb to be is also present in the sentence.
She does the laundry on Saturdays. ...
You do a lot of hard work. ...
Past simple did
They did learn how to swim two years ago.
Simple Future (Will)
The simple future or "simple future" is used to describe actions to be carried out in the future, without the need to specify when.
In English this verb tense is usually expressed with the modalities "shall / will" or with the construction "be going to".
Don't worry, they will be here on time.
Will you be home for dinner?
I will see you next week
She did live in Japan last year.
You did work very hard last week.
Auxiliary Use "Did" We use the "Past Simple" tense to talk about actions that happened at a specific time in the past.
The word "did" is the past simple form of the verb "do" as can be seen in the list of the most commonly used irregular verbs in English.
I do my homework in the afternoon.
Verbo auxiliar en forma negativa:
I go to the school everyday
Estos tienen dos usos verbo "Hacer"
I do my homework everyday
Futuro going to (Future going to) I am going to dance
Futuro Continuo (Future Continuous) I will be dancing
Futuro Simple (Future Simple) I will dance
Copretérito (amaba, comía, subía) ...
Futuro (amaré, comeré, subiré) ...
Pretérito (amé, comí, subí) ...
Presente (amo, como, subo) ...