作者:Griggs Griggs 6 年以前
269
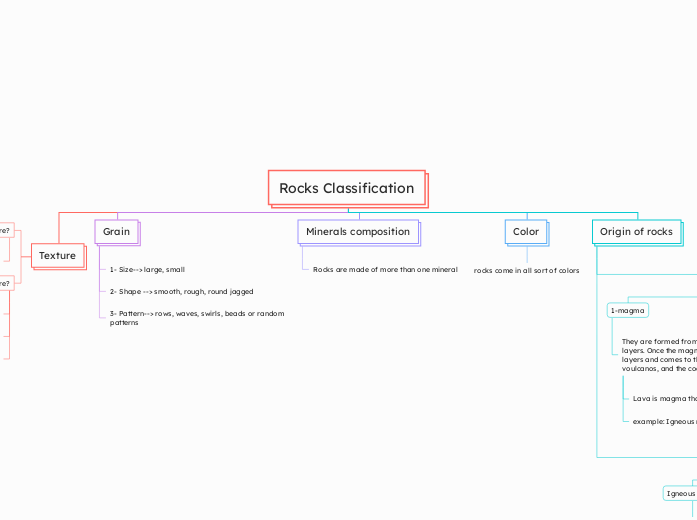
U2A1
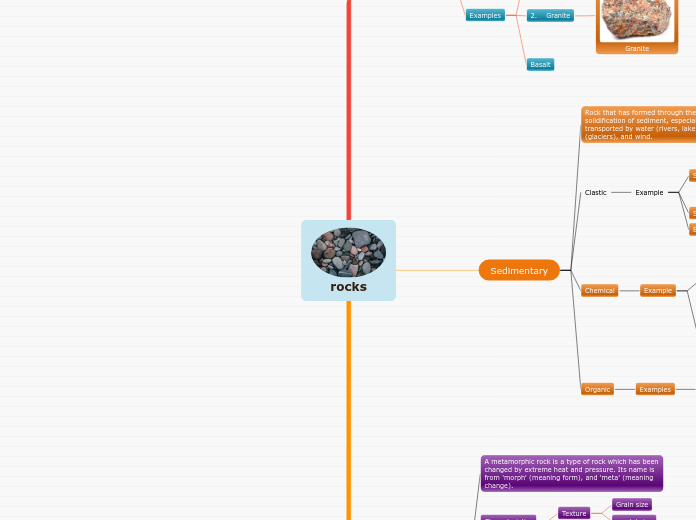
Igneous rocks are formed through the cooling and solidification of magma, either on the earth's surface or beneath it. When magma cools on the surface, it becomes extrusive, often resulting in rocks like basalt, which may contain vesicles formed by trapped gas bubbles.
開啟
Igneous Rocks felsic granite and rhyolite magnesium and iron add colour variations light grey lots of minerals like quartz and feldspar acid intermediate sodium present more white than mafic plagioclase mafic basalt and gabbro pyroxene and calcium plagioclase dark grey mostly in oceans basic extrusive magic, intermediate or felsic formed by volcanoes intrusive rocks Dunite and peridotite less than 45 percent silica are green and black contain olivine and pyroxene form in the mantle when viscous gas bubbles remaining are called vesicles gas can be released easily usually becomes basalt levels of viscosity the higher the silicon dioxide level the more viscous higher the temp the less viscous Extrusive Magma cools and crystallizes on the earths surface Volcanic vocab pyroclasts: airborne fragments from a volcano tephra: term for all airborne particles from a volcano pilian eruptions: produce dacitic or rhyolitc lava silica content Mafic also called basic has a low silica content and a high iron and magnesium content felsic also called acidic has a high silica content and a low iron and magnesium content eight minerals that form ingneous rocks Feldspar has two different types- sodium plagioclase and calcium plagioclase olivine, pyroxene, amphibole, biotite, orthoclase, muscovite, quartz, feldspar how ingenious rocks are formed when it cools it solidifies to form igneous rock such as granite or basalt when magma reacts the surface it is called lava inside earth is molten magma places ingneous rocks are found volcanic arcs- andesite and diorite continets- granite ocean plates- basalt and gabbro explosive vs non-explosive Strombolian are short and eruptive that burst viscous basaltic lava non explosive are called Hawaiian eruptions Volcanic eruptions are based on height of plume head height of eruptive column degree of fragmentation of the airborne volcanic products volume of material Different Types of Cooling Slow followed by fast porphyritic texture smooth grained crystal matrix and large crystal structure larger and smaller crystals Very fast results in glass elements are frozen in place no minerals grow Hours to days Fast aphanitic texture fine grained mineral textture microscopic in size Happens at earths surface Days to weeks Slow phaneritic texture mineral can be seen with naked eye below earths surface thousands to millions of years Intrusive Magma cools and crystallizes within the earth Plutonic