Why Do We Study
Food Science?
FOOD BORNE ILLNESSES
Listeria
Throw away foods that have passed their
expiration date
Salmonella
Cook foods properly to and prevent
cross-contamination to avoid this
E. coli
Prevented by properly cooking foods
and preventing cross-contamination
NUTRIENTS AND THEIR BENEFITS
Minerals
Dietary Fiber
Improves gut health
(provides good bacteria)
Controls blood sugar levels
Reduces cholesterol
Maintains bowel health and
regulates bowel movements
Aids body in healing itself
Improves strength and muscle mass
Reduces blood pressure
Lessens cravings that lead to
overeating and unhealthy food choices
Water
Improves digestion
Provides energy by
dissolving nutrients
Increases skin health
Vitamins
Support bones and
help heal wounds
Strengthen immune system
Repair cell damage
Convert food into energy
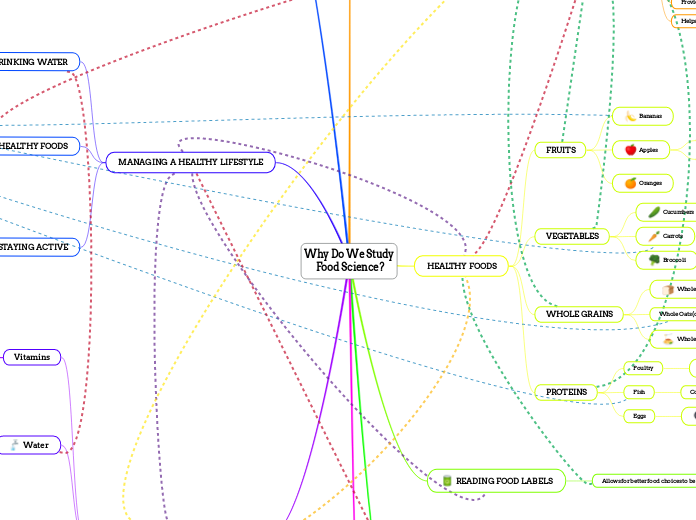
MANAGING A HEALTHY LIFESTYLE
STAYING ACTIVE
Physical Activities
Swimming
Helps in gaining muscles strength
and endurance
Sports
Soccer
Increases endurance and muscle
strength and betters heart health
Hockey
Improves heart health and
keeps your body moving
Walking/Running
Good for your cardiovascular
(heart) health
EATING HEALTHY FOODS
Proteins
Source of energy and contain amino acids
Whole Grains
High in fiber and help reduce the
risk of health problems (example: various cancers)
Vegetables
Source of vitamins and minerals
Fruits
Contain vitamins and minerals
DRINKING WATER
Prevents dehydration
Improves skin health
Dissolves nutrients and gives us energy
Helps with digestion
UNHEALTHY FOODS
'JUNK' FOOD
Linked to poor mental health
Could cause digestive issues
May cause disease
Various cancers
Increases risk of obesity
FAST FOOD
High in calories
High in saturated and
trans fats
Usually never includes
fruits or vegetables
Low in nutrients
High in sodium
FOOD SAFETY
STORAGE
To keep food from spoiling ...
Use ice packs to keep food cool when there is no fridge available
Thaw foods in the microwave or fridge
Use the fridge as a place to marinate foods
Place cooked/prepared foods in the fridge
within 2 hours
TIMING
Always ensure that your meats are
cooked properly and thoroughly to
avoid certain food borne illnesses
or food poisoning
SEPARATION
To avoid cross-contamination and food borne illnesses ...
Store raw meat in sealed containers or plastic bags
to keep them separated from other foods
Separate raw meat and seafood from other
food items in your shopping cart/bag and fridge
Place cooked food on a clean plate
Use different cutting board for raw
meats and other foods
CLEANLINESS
Clean/sanitize surfaces and cooking
materials after use
Wash fruits and vegetables
Wash hands before handling food
READING FOOD LABELS
Allows for better food choices to be made
HEALTHY FOODS
PROTEINS
Eggs
Fish
Contain minerals, calcium, and vitamins
Poultry
WHOLE GRAINS
Whole Wheat Pasta
Whole Oats (oatmeal)
Lots of fiber, vitamins and minerals,
and antioxidants
Whole Rye Bread
VEGETABLES
Broccoli
Carrots
Contain antioxidants and Vitamin A
Cucumbers
FRUITS
Oranges
Apples
Lower the risk of diseases
Lots of antioxidants and fiber
Bananas
IMPACTS CERTAIN FOODS HAVE ON OUR HEALTH
Positive Impacts
(healthy foods)
Helps in maintaining a healthy weight
Provides energy
Improves health of gut
Aids the digestive system
Improves overall mood
Walnuts
Berries
Lowers risk of disease
May help you live longer
Strengthens bones, teeth and muscles
Helps boost immune system
Negative Impacts
(unhealthy foods)
May cause poor mental health
Depression
Impact dental health
Ruin tooth enamel
Cavities
Increase cholesterol levels
From foods containing trans fats
Acne
Resulting from high amounts
of carbs and sugars
Higher risk of headaches
Caused by large sodium intakes
Bloating
Due to retaining water
Increases blood sugar
From eating empty carbohydrates
Disease/Illness
Type 2 Diabetes
Heart disease
Types of cancers
Weight gain
Obesity