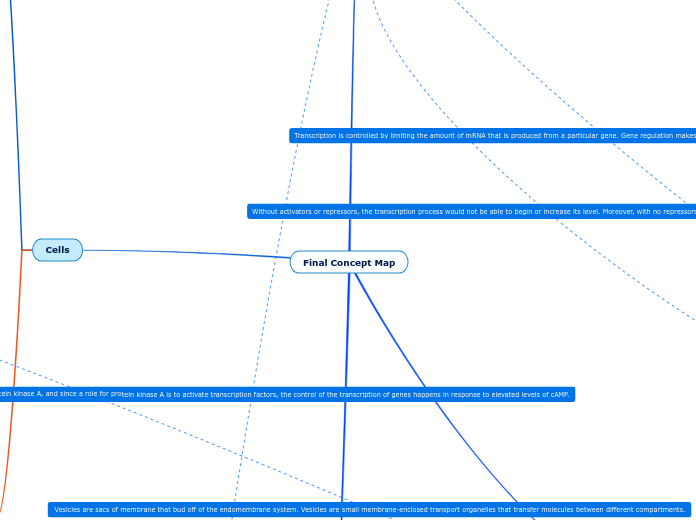
Biology: Concept Map
Gene Expression
Translation
Occurs in cytoplasm
Begins with mRNA
Binds to anti codon
Contains tRNA
contains amino acids
make protein
Can fit two ribosomes
Contains codons
Transcription
Occurs in nucleus
starts with DNA
unzipped by RNA polymerase
Creates mRNA
Replication
uses enzymes and proteins
Primase
Starting point for DNA synthesis
Synthesizes short RNA primers
SSB
Keeps DNA strands separated
DNA polymerase
adds nucleotides
in 5'->3' direction
Topoisomerase
Prevents DNA from recoiling
DNA helicase
Replication fork is formed
lagging strand
discontinuously synthesised
RNA primase creates
RNA primer
DNA polymerase replicates primer
Okazaki fragments are linked
By
DNA Ligase
forming leading strand
by DNA polymerase
RNA primase synthesizes RNA primer
strand is continuously synthesized
unzips DNA helix
Cell Signaling
Second Messangers
Enzyme
Created
Adenylyl Cyclase
G-Protien linked receptor(in membrane)
Non protien signaling pathway
Glycogen breakdown with epinephrine
Example
Cyclic AMP (cAMP)
Ion Channels
Ligand Gated
allows
Calcium Ions
Into
Cytoplasm
From
Mitochondrial Matrix
Protein Phosphorylation
Cell Reproduction
Phosphate
Activates
from ATP
Protein Kinase
Reversal Enzymes
Protein Phosphotases
Long Distance Signaling
Horomones
Local Signaling
Binds with
Signal Molecule
Ligand
Paracrine (growth Factor)
Synoptic neuro transmitters
Short Distance
3 Steps
Response
Triggers
Specific cellular response
Regulates
Nuclear transcription
Cytoplasmic Activity
Cell Metabolism
Transduction
2 Types
Single Step
Series of Change
Reception
Targets
Cell Detections
Protein Traffic
Golgi Apparatus
Which has a cis face
Protein then travels with cisternae
Is a specific vesicle
To the trans face
Protein exits and travels with a vesicle
Has a specific "tag"
Directed to the cytoplasm using a motor protein
Travels on microtubles
Arrives at the
Rough ER
Protein undergoes glycosylation
Adds a carbohydrate group
Forms a glycoprotein
Which through a vesicle to the
Plasma membrane contains
SRP Receptor
binds to the
SRP protien
binds to
Protiens
to synthesize
RNA
use
Ribosomes
Contain
ER Sequence
Are found in
Cytosol
Lumin
Plasma Membrane
Exocytosis