af Aqlan Syakir 4 år siden
253
CSC443
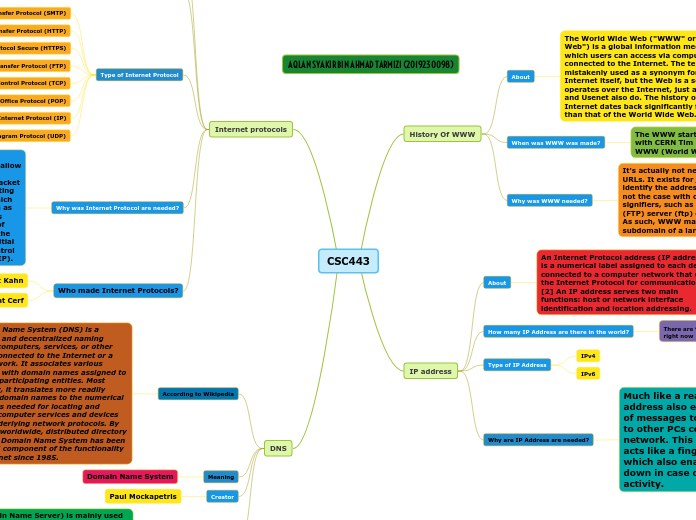
The Domain Name System (DNS) is essential for the functionality of the Internet, providing a hierarchical and decentralized way to associate domain names with numerical IP addresses.
af Aqlan Syakir 4 år siden
253

Mere som dette
Subtopic