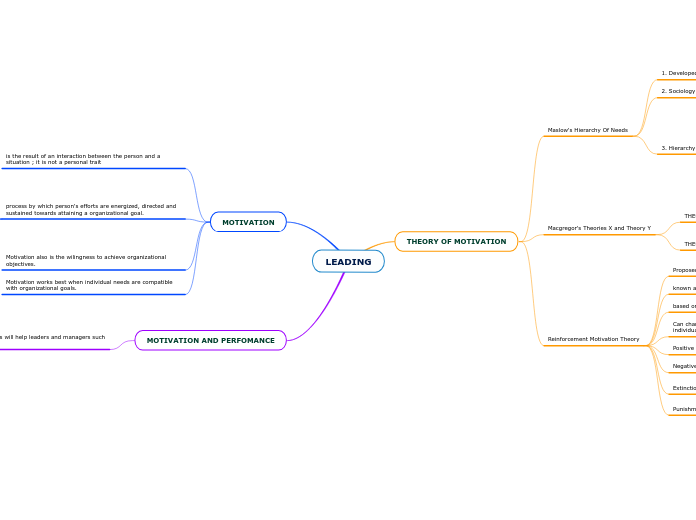
LEADING
MOTIVATION AND PERFOMANCE
Good motivation practices will help leaders and managers such as:
3. Encourage your subordinates to set perfomance goals that are specific, challenging and attainable.
2. Increase your employees' expectation that their efforts will lead to effective performance
1. be sensitive to the difference in needs and values among the people you supervise.
MOTIVATION
Motivation works best when individual needs are compatible with organizational goals.
Motivation also is the wilingness to achieve organizational objectives.
process by which person's efforts are energized, directed and sustained towards attaining a organizational goal.
Subtopic
Persistence
Directions
Energy
is the result of an interaction between the person and a situation ; it is not a personal trait
THEORY OF MOTIVATION
Reinforcement Motivation Theory
Punishment reinforcement
applying undesirable consequence
Extinction reinforcement
implies lowering the probability undesired behaviour by removing reward for that kind of behavioral
Negative reinforcement
avoidance
Positive reinforcement
giving positive response
Can change the direction, level and persistence of an individual's behaviour
based on "law of effect"
known as Behaviorism or Operant Conditioning
Proposed by Harvard psychologist B.F.Skinner.
Macgregor's Theories X and Theory Y
THEORY Y
Basically positive view. Assumes that workers can exercise self-direction, desire responsibility and like to work.
THEORY X
Basically negative view. Assumes that workers have little ambition, dislike work, avoid responsibility and require close supervision.
Maslow's Hierarchy Of Needs
3. Hierarchy of five needs :
v. Self - actualization needs.
iv. esteem needs
iii. Social needs
ii. Safety needs
i. Pgysiological needs
2. Sociology and behavioral psychology
1. Developed by Abraham Maslow