INTEGRANTES: Heidy Alfonso, Miguel Alarco, Johan Cárdenas, Carlos Guevara, Valentina Muñoz, Anderson Duque y Paula Osorio
Abordajes: Rounge - denker, degloving facial y combinados craneofaciales
TRATAMIENTO
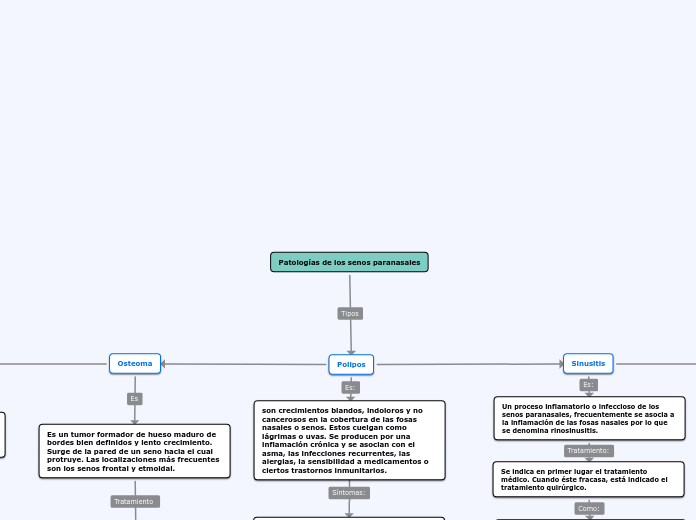
PATOLOGÍAS LOS SENOS PARANASALES
The part of speech is a category to which a word is assigned according to its syntactic functions. In English the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
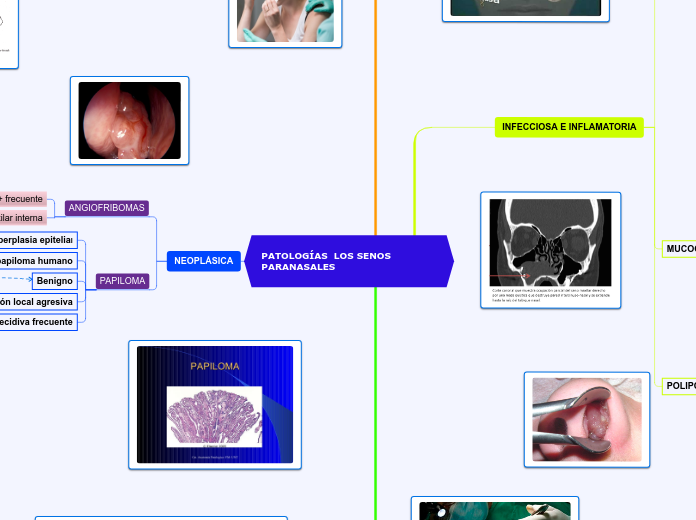
NEOPLÁSICA
An interjection is used to express emotion in a sentence.
Think of other interjections!
PAPILOMA
A conjunction is a word like 'if' 'but' or 'and' which is used to connect sentences or clauses together.
Recidiva frecuente
Causa de destrucción local agresiva
Benigno
Virus del papiloma humano
Subordinating conjunctions are conjunctions that are used at the beginning of subordinate clauses. Some examples of these conjunctions are: although, after, before, because, how, if, once, since, so that, until, unless, when etc.
Hiperplasia epitelial
Coordinating conjunctions always connect phrases, words, and clauses. They are: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so.
ANGIOFRIBOMAS
A numeral is a word or phrase that describes a numerical quantity.
Some theories of grammar use the word 'numeral' to refer to cardinal numbers that act as a determiner to specify the quantity of a noun, for example the 'two' in 'two hats'.
Arteria maxilar interna
Tumor benigno juvenil + frecuente
PROCEDIMIENTOS QURÚGICOS
A noun is defined as a person, place, thing or idea. Proper nouns always begin with a capital letter. Common nouns, which are general words, such as 'cars,' are not capitalized.
SENO ESFENOIDAL
Compound nouns are words where two nouns have been stuck together to make a new noun. Compound nouns should be written as one word, without a hyphen.
Esfenoidotomía
Abordaje: Transpterigoideo
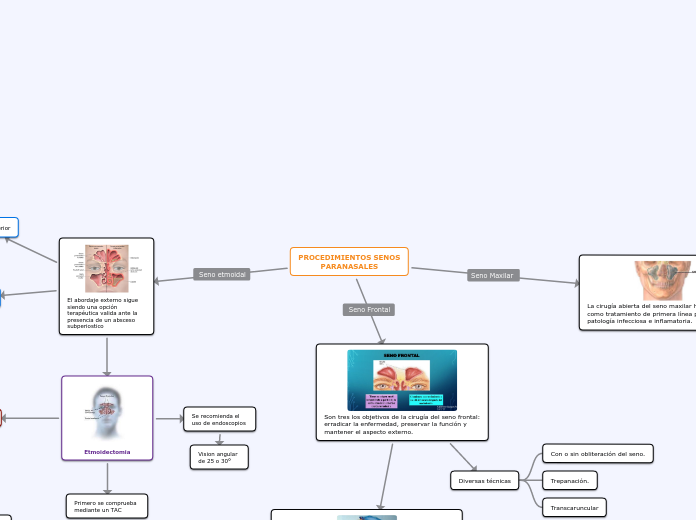
SENO FRONTAL
A noun which refers to a group of things/people.
Lynch
Frontoetmoidectomía
Abordaje: Craneofacial combinado
Degloving
Abordaje: Sublabial
SENO MAXILAR
Countable nouns are nouns that can be counted, even if the number might be extraordinarily high.
Uncountable nouns are nouns that come in a state or quantity which is impossible to count; liquids are uncountable, as are things which act
like liquids.
Osteoplastia frontal
Abordaje: bicoronal
Maxilectomía
Caldwell - Luc
SENO ETMOIDAL
Proper nouns are the names of specific people or places. They should always begin with a capital letter.
weber- ferguson
Abordaje: Transetmoidal, transfacial
Etmoidectomía
Abordaje: Paralateronasal
INFECCIOSA E INFLAMATORIA
An adjective is a word that's used to describe a specific noun and to provide more detail to the listener.
POLIPOSIS
Lesiones
An article is a word used to modify a noun, which is a person, place, object, or idea. Technically, an article is an adjective, which is any word that modifies a noun.
Crónica no maligna
Gelatinosas
Indefinite articles are the words 'a' and 'an.' Each of these articles is used to refer to a noun, but the noun being referred to is not a specific person, place, object, or idea. It can be any noun from a group of nouns.
Lisas
It refers directly to a specific noun or groups of nouns.
Masa laterales del etmoides
Degeneración edematosa
MUCOCELE
Piomucocele son los sobre infectados
Frontoetmoidal + común
Obstrucción de los ostium
Desgaste de la pared por acumulación de secreciones
Lesión quística crónica del seno
SINUSITIS
Superlative adjectives demonstrate a higher level of comparison between entities.
COMPLICACIONES
Endocraneanas
Trombosis del seno orbitario
Orbitarias
Mucocele
Superlative
CLASIFICACIÓN
The personal pronouns are I, you, he, she, it, we, they. More often than not (but certainly not always), they replace nouns representing people.
Evolución
Crónicas
Quirúrgico
Subagudas
Agudas
Vasoconstrictores
Corticoides
Antibioterapia
Criterio anatómico
Inflamación de la mucosa de los senos paranasales, obstruyendo los meatos y produciendo acumulo de secreciones
4. Alteraciones anatómicas
3. Consecuencia de un trauma
2. Alérgico
1. Infeccioso
DEFINICIÓN Y FUNCIÓN
A verb is an action word or 'doing' word that signifies movement in some way.
Actúan como cajas de resonancia para la voz
An auxiliary verb helps the main (full) verb and is also called a 'helping verb.' With auxiliary verbs, you can write sentences in different tenses, moods, or voices.
Colaboran con la humedificación y contaminación del aire
A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective or to create a verb tense. There are two types of participles: Present participle (ending -ing) and Past participle (usually ending -ed, -d, -t, -en, or -n).
drenar secreciones para su auto-limpieza
A modal is a type of auxiliary (helping) verb that is used to express: ability, possibility, permission or obligation. The main modal verbs in the English language are: can, could, may, might, must, shall, should, will, would.
Se encuentran en los huesos frontales, esfenoides, etmoides y maxilar superior
A linking verb connects the subject with a word that gives information about the subject, such as a condition or relationship.
Conjunto de cavidades aéreas que están en una relación íntima con las fosas nasales
A verb with its own meaning: a verb that is not an auxiliary verb.