Prosocial behavior
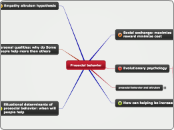
Situational determinants of prosocial behavior: when will people help
Effects of media: Video games and song lyrics increase helping
Communal relationship vs exchange relationship
In general we are more likely to help in a Communal relationship than an exchange relationship except if our self esteem is threatened then we are more likely to help the stranger.
The more bystanders the less likely to help
Residential mobility: longtime one place
Rural vs urban
Personal qualities: why do Some people help more than others
Effect of mood
Sad, negative state relief hypothesis
Feel bad, do good
Guilt to cancel bad deeds
feel good, do good
Cultural differences
ingroup-empathy, outgroup-furthers self interest
Gender differences
males heroic acts, females long term relationships commitment
Altruistic personality
Qualities
not much more likely to help
Empathy altruism hypothesis
we will help if we feel empathy
If not we will help if benefits outweigh costs
we will help purely for altruistic reasons regardless of gain
How can helping be increased?
Increasing Volunteerism
must not be imposed to avoid over justification effect
Awareness of bystander effect
prosocial behavior and altruism
Any act performed with goal of benefiting another person
Altruism desire to help even if it involves cost to helper
Evolutionary psychology
Reciprocity norm: helping others will increase the likelihood that they will help us in future
kin selection: behaviors that help genetic relative are favored
Social exchange: maximize reward minimize cost
true altruism does not exist
People help when benefits outweigh costs
cost
danger,pain, embarrassment, time
Reward
reciprocity, relief, self worth