af Solangie Dueñas 4 år siden
336
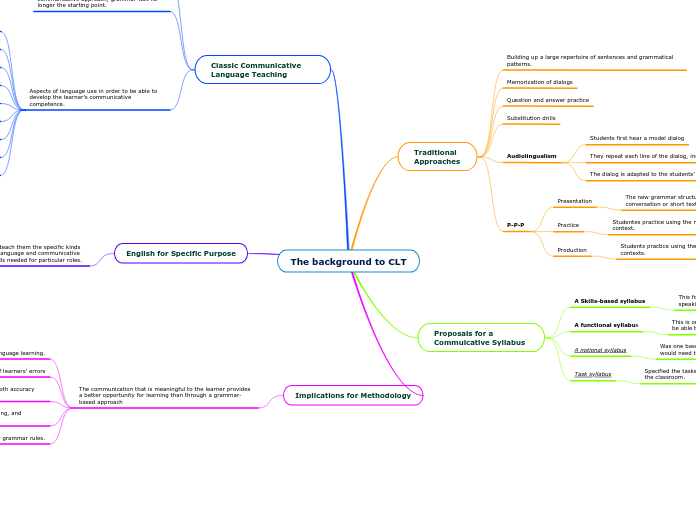
The background to CLT
The approach to teaching English has evolved to include various methods tailored to specific needs, highlighting the importance of Communicative Language Teaching (CLT) and English for Specific Purposes (