This makes sense because
as you go down a period in
the table of elements, and the
atomic number increases, the
ionization energy increases,
the electron affinity decreases,
the effective nuclear charge
increases, and the atomic
radius decreases.
These periodic trends exist because
all atoms in a period have similar
structures and only vary slightly from
each other. With an extra electron in
each atom down the period, the structure
of each atom changes slightly and creates
these trends. With an added electron, but the same number of orbitals, atoms have more of a shielding effect repelling other atoms from the nucleus. This is until the atoms that almost have a full valence shell of electrons and gain them more easily than lose them. This is why when certain trends increase going down the period, other trends decrease.
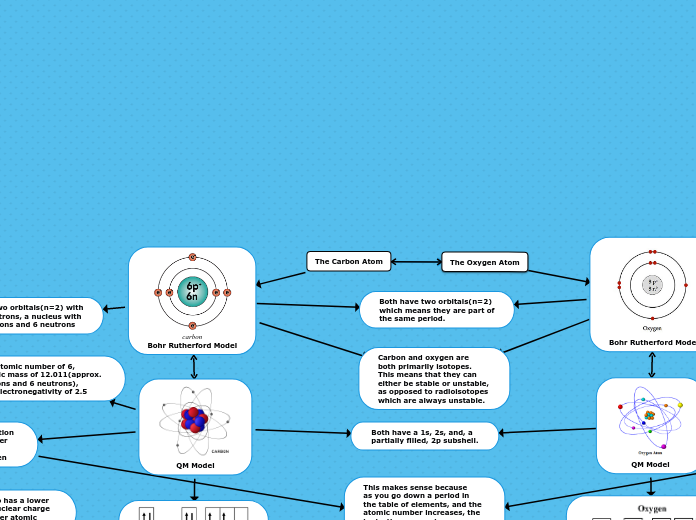
Bohr Rutherford Model
Both have two orbitals(n=2)
which means they are part of
the same period.
Has two orbitals(n=2) with 8 electrons,
a nucleus with 8 protons and 8 neutrons
Has 6 valence electrons
making it more reactive
than carbon
Has a greater Ionization energy and
a lower electron affinity than carbon
Oxygen has a greater effective nuclear
charge and a lower atomic radius than
carbon
Has an atomic number of 8, an
atomic mass of 15.999(approx. 8
electrons and 8 neutrons) and an
electronegativity of 3.5
The Carbon Atom
carbon
Bohr Rutherford Model
Carbon and oxygen are
both primarily isotopes.
This means that they can
either be stable or unstable,
as opposed to radioisotopes
which are always unstable.
Has two orbitals(n=2) with
6 electrons, a nucleus with
6 protons and 6 neutrons
Has 4 valence electrons making
it less reactive than oxygen
QM Model
Has a lower ionization
energy but a greater
electron affinity
compared to oxygen
Carbon also has a lower
effective nuclear charge
and a greater atomic
radius than oxygen
Has an atomic number of 6,
an atomic mass of 12.011(approx.
6 electrons and 6 neutrons),
and an electronegativity of 2.5
Both have a 1s, 2s, and, a
partially filled, 2p subshell.
Carbon
The Oxygen Atom