tight junctions
long distance signaling
travel in bloodstream
plasmodesmata
gap junctions
paracrine signaling
secretory vesicle
extracellular fluid
synaptic signaling
electrical signals
synapse
dimer
ATP is hydrolyezed to ADP
phosphate groups are added
phosphorylated dimer
2 inactive relay proteins to attach
Subtopic
inactive
ligand-gated ion channel receptor
closed
bound with ligand
activates the channel
flow of specific ions
intramembrane space
rapid change of concentration
an action potential
a cellular response is generated
Cell Signaling
reception
ligand binds to receptor
on the membrane
transduction
plasma membrane
series of enzyme activations
chemical signals
response
Ion Channels
G Protein Linked
G protein coupled receptor
G protein
Adenylyl Cyclase
enzyme
cAMP
second messenger
Protein Kinase A
phosphorylation cascade
cellular response is generated
GDP is bound
GTP is bound
ligand attaches to binding site
neurotransmitters
protein hormones
Tyrosine Kinase
2 tyrosine kinase proteins
ligand binds to binding site
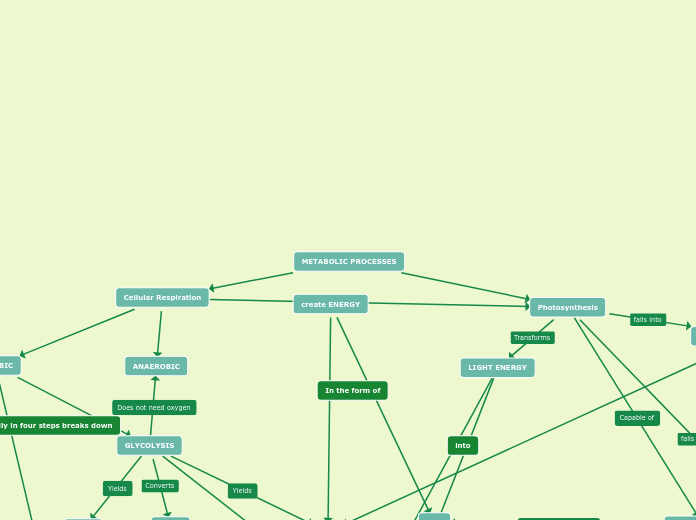
Processes of ATP formation
Photosynthesis
stage 1
cellular respiration
Takes place in the cytosol
Takes place on the mitochondria
26-28 ATP
ATP Synthase
H+ gradient
Chemiosmosis
H+ pump into innermembrane space
Cyt c
Complex 4
Complex 3
Q
Complex 2
Complex 1
Alpha ketogluterase
Isocitrate
Citrate
Oxaloacetate
Acetyl CoA
Pyruvate
Phosphofructokinase
Hexokinase
Fructose 1, 6- Biphosphate
Fructose 6 Phosphate
Glucose 6-Phosphate
C6H12O6 + 6O2 —> 6CO2 + 6H2O + ATP
Glucose
Oxygen
Pyruvate Oxidation
Electron Transport Chain (ETC)
Kreb’s Cycle
Citric Acid Cylcle
Glycolysis
Cell Respiration
Functions of
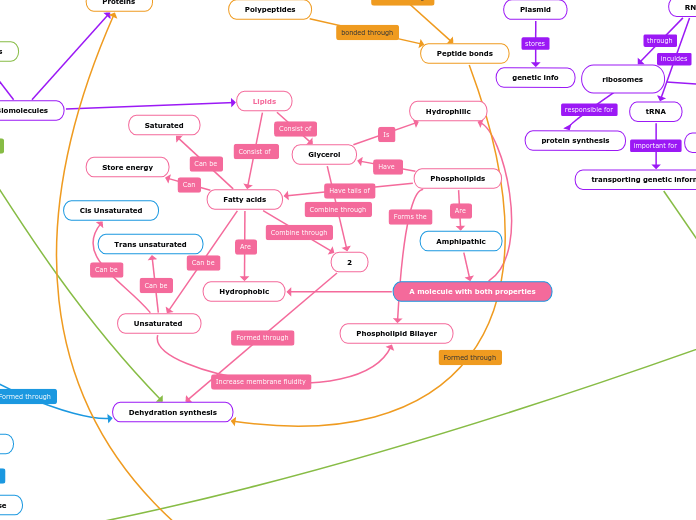
Trans unsaturated
Cis Unsaturated
A molecule with both properties
Amphipathic
Phospholipids
Backbone
Anti parallel
Strands
Cytosine
Guanine
Adenine
Thymine
Uracil
Ribose
Nucleosides
Code for proteins
Inheritence
Nitrogenous Base
Phosphate Group
Deoxiribose
Pentose Sugar
Hydrogen bond
Phosphodiester bond
DNA
Nucleotides
capsule and slime layers
defense and adhesion
unicellular
Cells
Plasma Membrane
High to low concentration
Along concentration gradient
ATP is not required
Passive
Diffusion
Facilitated
Proteins aid in transport
Hydrophobic
Amino acids with nonpolar R groups
Hydrophilic
amino acids with polar R groups
Osmosis
Water from high (through semi-permeable membrane) to low concentration until water is equal on both sides of plasma membrane
Water Balance
Hypotonic
rapidly gain water
turgid
swell until the wall opposes uptake
Solution has lower solute concentration than another solution
Water particles move into cell, cell explands & eventually lyses
Isotonic
water will not flow in or out
ideal state
flaccid
no net movement inside cell
Same solute concentration as another solution
Overall concentration on both sides of cell membrane is constant
Hypertonic
water molecules within cells diffuse out & the solute molecules enter, making cell shrink
Plasmolyzed
membrane pulls away from wall
plasmolysis
Higher solute concentration than another solution
Water particles move out cell
Simple
Small nonpolar molecules can pass through
Polar molecules have some trouble passing through
Ions cannot pass through
Low to high concentration
Against concentation gradient
ATP required
Active
Vesicles
Small sac-like organelles that store & transport materials inside cell
Substance entering cell
Endocytosis
Receptor-Mediated cytosis
Specialized type of pinocytosus enabling cell to acquire bulk amounts of specific substance
Phagocytosis
Solid particles into cell through formation of membrane vesicle
Pinocytosis
Cell takes in fluids along with dissolved small molecules
Substance leaving cell
Exocytosis
outward transport of large particles via vesicle which fuses with cell membrane
Sodium potassium pump
proteins aid Na+ & K+ across the membrane
Secondary
Primary
Eukaryotes
cell membrane
phospholipid bilayer
hydrophilic head and hydrophobic tail
amphipathic
selectively permeable membrane
small, nonpolar molecules
Eukarya
animal cells
plant cells
vacuole
cell sap
storage of materials and water
cellulose
chloroplasts
green color
Prokaryotes
RNA
mRNA
sending messages in the cell
tRNA
transporting genetic information
rRNA
translating messages
ribosomes
protein synthesis
flagella and cilia
movement
membrane bound organelles
rough ER
proteins
smooth ER
lipids, phospholipid and steroids
golgi apparatus
transporting and packaging proteins/lipids
lysosomes
waste removal
mitochondria
ATP
photosynthesis
energy for cell
cytoplasm
glycogen
gel like fluid
between cell membrane and nucleus
place where organelles can function
granules
energy
nucleus
genetic information
DNA/chromosomes
double helix
cell's activity
bacteria
cell wall
cell structure
peptidoglycan
archaea
extremely hot environments
circular DNA
Plasmid
genetic info
Nucleic Acids
Ionic bonds
Hydrophobic Interactions
Disulfide bonds
Intermolecular bonds
Intramolecular bonds
R Groups
Quaternary Structure
Hydrogen bonds
Beta sheets
Alpha helices
Amino acid sequence
Tertiary Structure
Primary structure
Secondary Structure
Levels of Structure
Defense
Storage
Transport
Enzymes
Peptide bonds
Polypeptides
Amino acids
Proteins
Store energy
Phospholipid Bilayer
Saturated
Unsaturated
Glycerol
Fatty acids
Lipids
Biomolecules
Carbohydrates
null
Beta glucose
Alpha glucose
Cellulose
Amylose
Amylopectin
Glycogen
Structure
Storage molecules
Dehydration synthesis
Glycosidic linkages
Polysacharides
Monosacharides
2