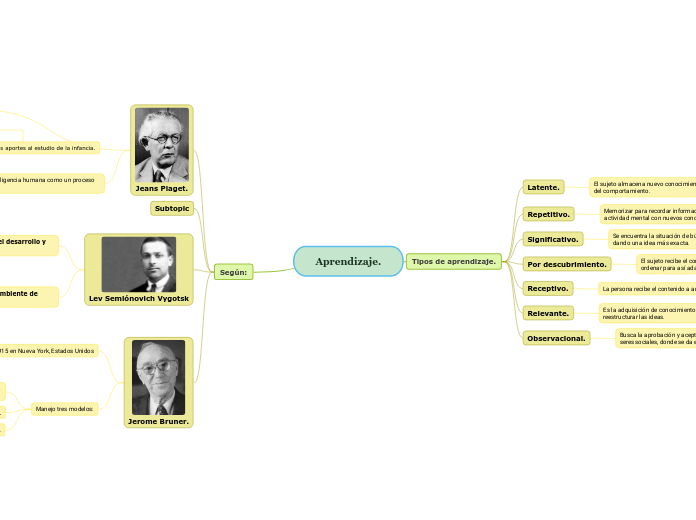
Aprendizaje.
Tenses demonstrate the time of actions centered around the subject of the sentence. These actions are called verbs and change according to tenses.
Según:
There are four Future tenses:
- Future Simple ('with Will' and 'with Going to')
- Future Continuous
- Future Perfect Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
Jerome Bruner.
Future Continuous is used:
- for an action that is likely to happen in the future and continue for an expected length of time
- for an action that will be in progress at some point in the future
- for action verbs (e.g. running)
- for predictions about future events
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow at 5 o'clock)
Manejo tres modelos:
Structure:
Subject + Won’t Be + Verb-ING
e.g. He won’t be having fun at the party.
Simbólico: Hace uso de la palabra escrita y hablada.
Icónico: Se emplea dibujos o imágenes.
Enactivo: Se aprende actuando, imitando y manipulando objetos.
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of word "to be":
I will not be beingYou will not be beingHe/She/It will not be beingWe will not be beingYou will not be beingThey will not be being
Form of word "to have":
I will not be havingYou will not be havingHe/She/It will not be havingWe will not be havingYou will not be havingThey will not be having
Nació el 1 de octubre de 1915 en Nueva York, Estados Unidos
Structure:
Subject + Will Be + Verb-ING
e.g. You will be having fun at the party.
Además, explica aspectos importantes sobre el aprendizaje de los seres humanos.
Psicólogo estadounidense que hizo importantes contribuciones a la psicología cognitiva.
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I will be beingYou will be beingHe/She/It will be beingWe will be beingYou will be beingThey will be being
Form of verb 'to have':
I will be havingYou will be havingHe/She/It will be havingWe will be havingYou will be havingThey will be having
Lev Semiónovich Vygotsk
Future Simple is used:
- to predict an event in the future
- to invite
- to give orders
- to express willingness
- for actions that have not yet occurred but that will occur at a future date
El aprendizaje se desarrolla en un ambiente de interacción
'Going to' Future is used:
- to talk about our future intentions and plans
- for commands
Some adverbs used with 'Going to' Future:
- later
- tonight
- tomorrow
- next week
- next month
- next year
También permite la reconstrucción de significados.
Structure:
Subject + BE not + going to + Infinitive Form of Verb
e.g. He isn't going to spend his vacation in Hawaii.
Ello impulsa al desarrollo de habilidades mentales por medio del descubrimiento y la interiorización.
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + going to + Infinitive Form of Verb
e.g. She’s going to be a professional dancer when she grows up.
Es un autor clave en la psicología del desarrollo y de la educación.
Future Simple with 'will'' is used:
- to predict the future
- for something with absolute certainty
- when we're talking about a decision at the moment of speaking
- promises, requests, refusals, offers
- future facts
Some adverbs used with Future Simple:
- tomorrow
- next week
- next month
- next year
Un autor único que desarrolló teorías en torno a la educación y la infancia
Structure:
Will + Subject + V1(First Form of Verb)?
e.g. Will you see Mary when she comes back from Denmark?
La vida profesional de Vygotsky se focalizó principalmente en la psicología del desarrollo y en la filosofía educativa.
Structure:
Subject + Won’t (will not) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. You won’t see Mary when she comes back from Denmark.
Subtopic
Jeans Piaget.
Future Perfect Simple is used for:
- an action that will be finished by a particular time in the future
- an action that starts before and continues up to another action or time in the future
- an action that will finish before a certain time in the future, but it is not known exactly when
Adverb used with Future Continuous:
- tomorrow (e.g. tomorrow by 7)
Propone el concepto de inteligencia humana como un proceso de naturaleza biológica.
El suizo sostiene que las estructuras biológicas determinan aquello que somos capaces de percibir y comprender.
Epistemólogo y biólogo suizo
Structure:
Subject + Will Have + Past Participle
e.g. I will have met my friend form United States by this time tomorrow.
Reconocido por sus aportes al estudio de la infancia.
Presentó la teoría constructiva del desarrollo de la inteligencia.
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb 'to be':
I will have beenYou will have beenHe/She/It will have beenWe will have beenYou will have beenThey will have been
Form of verb 'to have':
I will have hadYou will have hadHe/She/It will have hadWe will have hadYou will have hadThey will have had
Tipos de aprendizaje.
There are four Present tenses:
- Present Simple
- Present Continuous
- Present Perfect
- Present Perfect Continuous
Observacional.
Busca la aprobación y aceptación de otros individuos como seres sociales, donde se da el cambio de conducta.
Integrantes GRUPO 3.
Josias Aaron Acevedo García.
Fernando Romaní Bendezu.
Gleber Moriano Medina.
Nery Humberth Mariategui.
Haydee Guerra Castillon.
Relevante.
Es la adquisición de conocimientos, habilidades y actitudes para reestructurar las ideas.
Receptivo.
La persona recibe el contenido a analizar.
Por ejemplo: La explicación de un profesor o información audiovisual, donde se recepcionan ideas concretas.
Por descubrimiento.
Present Perfect Continuous is used:
- to describe an action that started in the past and has continued up to the present
- to describe an action that has just finished
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect Continuous:
- always
- only
- never
- ever
- still
- just
El sujeto recibe el contenido y descubre conceptos que procede a ordenar para así adaptarlos.
Structure:
Have/ has + Subject + been Verb-ING?
e.g. How long has he been learning German?
Significativo.
Present Perfect is used for:
- an action that occurred at a time which is indefinite and has its effect on the subject
- an action that occurred many times and has the possibility to occur in the present/future
- an action that began in the past and is still going on in the present
Some adverbs used with Present Perfect:
- just
- already
- yet
- for
- never/ever
- up to now
Se encuentra la situación de búsqueda de nueva información, dando una idea más exacta.
Structure:
Have/ has +Subject+ Past Participle?
e.g. Has she finished the letter?
Repetitivo.
Present Continuous is used to indicate the ongoing time (now).
Some adverbs used with Present Continuous:
- now, right now
- at this moment
- at the moment
- continually
- perpetually
- this year
- this season
- forever
Memorizar para recordar información y tener una mejor actividad mental con nuevos conocimientos.
Structure:
Subject + BE (am/is/are) + Verb-ING
e.g. You are eating now.
Latente.
Present Simple is used for:
- habits
- general truths
- repeated actions of events
- fixed arrangements/timetables
- feelings/opinions/beliefs
- instructions.
Some adverbs used with Present Simple:
- always
- usually
- seldom
- never
- sometimes
- often
- frequently, generally
- habitually, occasionally
- once, twice
El sujeto almacena nuevo conocimiento sin importar el cambio del comportamiento.
Structure:
Subject (I, You, We, They) + V1(First Form of Verb)
e.g. I usually go jogging at weekends.
Subject (He, She, It)+ V1(First Form of Verb) + s/es
e.g. She writes every day.
No se necesita exhibir nuestro aprendizaje para uqe este ocurra. (Edward Tolmand, 1959).
Type in your own examples or you can also choose from the examples below.
Form of verb "to be":
I amYou areHe/she/it isWe areYou areThey are
Form of verb "to have":
I haveYou haveHe/she/it hasWe haveYou haveThey have