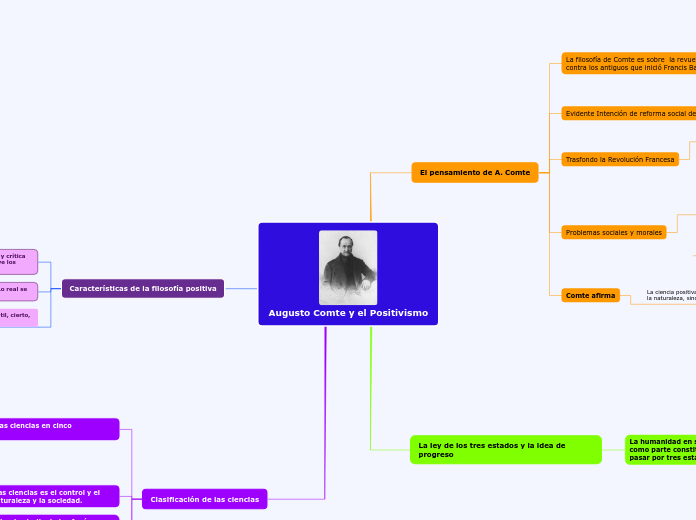
Augusto Comte y el Positivismo
In linguistics, syntax is the set of rules, principles, and processes that govern the structure of sentences in a given language, usually including word order.
Clasificación de las ciencias
A complex sentence is a sentence that contains an independent clause and one or more dependent clauses.
An independent clause can stand alone as a sentence, but a dependent clause even though it has a subject and a verb cannot stand alone.
La dictadura del mexicano Porfirio Díaz utilizó el positivismo:
An appositive clause follows another noun or noun phrase in apposition to it; that is, it provides information that further identifies or defines it.
como justificación teórica de su política
Esto produjo que la paternidad de Comte hacia la sociología y el positivismo haya sido reconocida a regañadientes
La sociología trata el estudio de los fenómenos sociales y de sus leyes como camino para explicar la evolución de la humanidad
A predicative clause may be introduced by conjunctions - that, whether, whether... or, as, as if, as though, because, lest, the way - or connectives.
The latter may be conjunctive pronouns - who, whoever, what, whatever, which - or conjunctive adverbs - where, wherever, when, whenever, how, why.
Y poder excluir todo posible cambio o revolución incontrolada
La finalidad de las ciencias es el control y el dominio de la naturaleza y la sociedad.
The object clause is a phrase on which a verb performs an action. It falls at the end of a sentence, and is governed by a verb or a preposition.
Comte clasifica las ciencias en cinco fundamentales:
The subject clause is a dependent clause that acts as a subject.
Sociología
Fisiología
Química
Fisica
Astronomía
Características de la filosofía positiva
A compound sentence is a sentence that has at least two independent clauses joined by a comma, semicolon or conjunction. An independent clause is a clause that has a subject and verb and forms a complete thought.
Lo positivo tiene como características el ser útil, cierto, preciso, constructivo y relativo
El término positivo hace referencia a lo real. Lo real se opone a todo tipo de esencialismo.
Create your own compound sentences, using the coordinators above.
Se define por oposición a la filosofía negativa y crítica de Rousseau y Voltaire a la que Comte atribuye los males de la anarquía
When independent clauses are joined with coordinators (also called coordinating conjunctions), commas and semicolons, they do more than just join the clauses. They add meaning and flow to your writing.
La ley de los tres estados y la idea de progreso
La humanidad en su conjunto y el individuo como parte constitutiva, está determinado a pasar por tres estados sociales:
See the example below and try to create your own simple sentences.
Tim drives the car.
El Estado positivo
A este estado le corresponde la sociedad industrial, capitaneada por científicos y expertos que asegurarán el orden social.
En este estado el hombre no busca saber qué son las cosas, sino que mediante la experiencia
La observación trata de explicar cómo se comportan.
El estado metafísico
Se cuestiona la racionalidad teológica
Lo sobrenatural es reemplazado por entidades abstractas radicadas
En las cosas mismas que explican su por qué y determinan su naturaleza
El Estado teológico
el hombre busca las causas últimas y explicativas de la naturaleza en fuerzas sobrenaturales
A través del fetichismo y, más tarde, del politeísmo y el monoteísmo.
El pensamiento de A. Comte
Comte afirma
The attribute is defined as a quality or characteristic of a person, place or thing.
La ciencia positiva podrá hallar las leyes que gobiernan no sólo la naturaleza, sino nuestra propia historia social
El progreso de estados sociales
La sucesión
Problemas sociales y morales
The predicative is defined as an adjective or noun forming or contained in the predicate.
Its main trait is that it serves to express a property that is assigned to a 'subject'.
For e.g.: The dog is old.
analizados desde una perspectiva científica positiva en la observación empírica de los fenómenos
Permita descubrir y explicar el comportamiento de las cosas en términos de leyes universales susceptibles
Trasfondo la Revolución Francesa
Traditional grammar defines the object in a sentence as the entity that is acted upon by the subject.
Comte acusa a los dos autores de generar utopías metafísicas
The indirect object identifies the person/thing for whom/which the action of the verb is performed.
The indirect object is usually a person or a thing.
Incapaces de otorgar un orden social
Evidente Intención de reforma social de su filosofía
The predicate of a sentence is the part that modifies the subject in some way. Because the subject is the person, place, or thing that a sentence is about, the predicate must contain a verb explaining what the subject does and can also include a modifier.
Adhiere una postura conservadora en enfrentamiento con las propuestas ilustradas de Voltaire y Rousseau
La filosofía de Comte es sobre la revuelta moderna contra los antiguos que inició Francis Bacon
The subject of a sentence is the person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb.
Ask the question, 'Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?' and the answer to that question is the subject.
Consistió en la asunción de la razón y la ciencia como únicas guías de la humanidad
Capaces de instaurar el orden social