von Annabel Granger Vor 6 Jahren
215
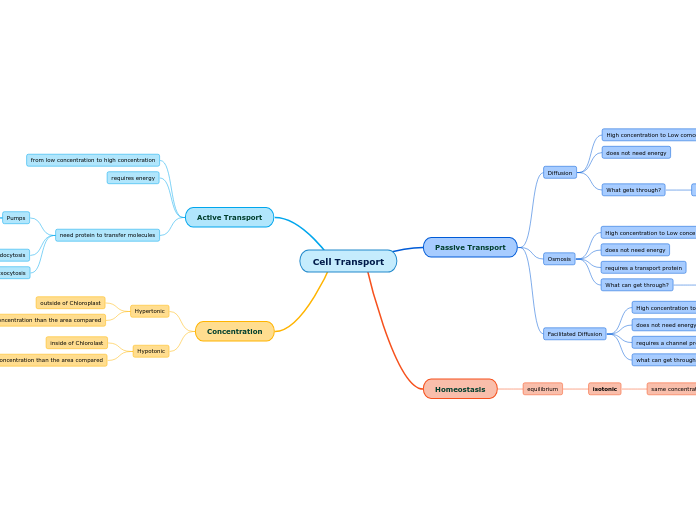
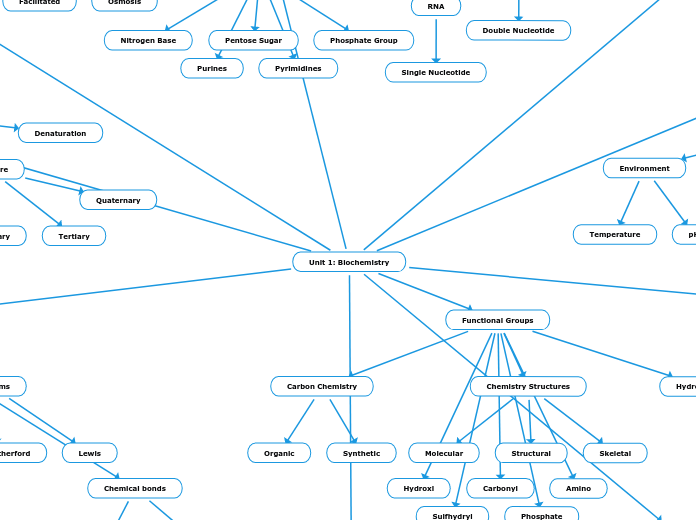
Granger - Blank Concept Map
Biological macromolecules play critical roles in living organisms, each with distinct characteristics and functions. Proteins are composed of amino acids linked by peptide bonds and are essential for various bodily functions such as immune response, transport, and movement.