von Ravi Chacko Vor 7 Jahren
1854
Immunology
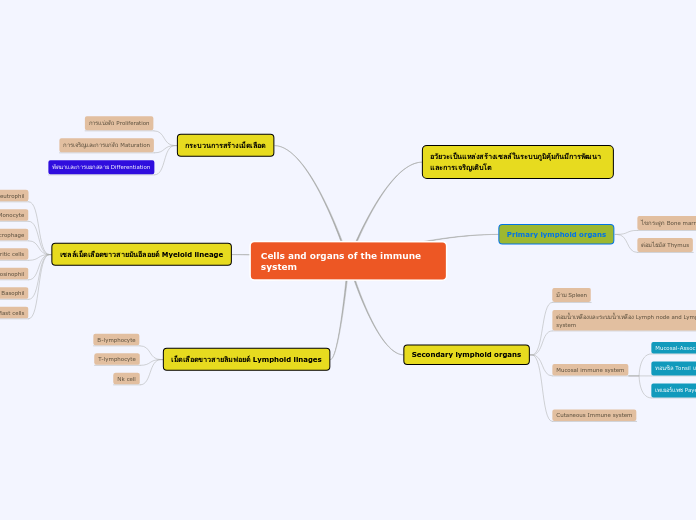
The immune system involves a variety of cells and mechanisms to protect the body against pathogens. Leukocytes, including basophils, neutrophils, and monocytes, play crucial roles in inflammation and phagocytosis.