von Ahmad Hakim Vor 4 Jahren
326
JOINTS
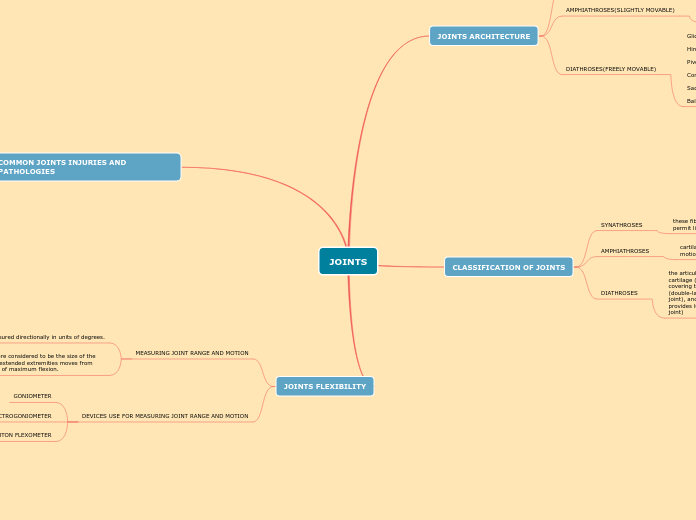
Various joint types in the human body are categorized based on their mobility, including diathroses (freely movable), synarthroses (immovable), and amphiarthroses (slightly movable)
von Ahmad Hakim Vor 4 Jahren
326

Mehr dazu