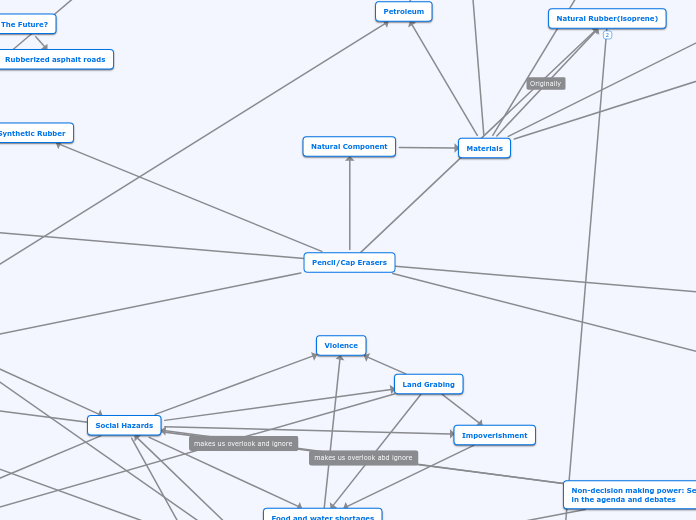
Pencil/Cap Erasers
Synthetic Rubber
Sustainable?
The Future?
Rubberized asphalt roads
Disposal/Environmental Hazards
Hard to track
Waste=Shavings too small
(straight to)Landfills
Sucked in by the vacuum cleaner
covered up with rest of municipal waste
can end up in the soil if it is rained on
ends up leachate
treated as wastewater
released into nearby water pool
end in waterways below the soil
Recycling not feasable
No specifically targeted recycling company
Shavings filled with graphite soot
Natural Component
Materials
Petroleum
Benzene
Vegetable Oil
Plasticizer
Abrasive
Pumice
Cheaper SBR (=Styrene-butadiene)
Fillers
Made up of 2 Types of Plastic
Plastic
Elastomers (Plastic treated with Chemicals)
good stability to aging
Additives
good resistance
Meaning families of synthetic rubber
Natural Rubber(isoprene)
Latex
Rubber Trees
Power Component
Biggest Problem
Erasers are not politicized
Those in power don't have to set the discourse anymore
No specific targeted Recycling Company for Erasers
Luke's 3 Dimensions of Power
Ideological Power: Influences one's wishes and thoughts-> makes them think differently from what they are used to
Non-decision making power: Set discourse in the agenda and debates
Social Component
Manufacturing places (e.g. for Faber Castell)
China
Malaysia
India
Brazil
Social Hazards
3 Types of Producers cultivating Rubber
Smallholder Farms
Private Enterpreneurs
State-owned companies and farms
Food and water shortages
Violence
Impoverishment
Land Grabing
Technologies/Chemical Process used
Distillation
Fluid Catalytic Cracking
Environmental Hazards
Polluted Water Pools
Chemical Smell Polution
Hazardous Waste
Soil Erosion
Loss of Biodiversity
Deforestation
''the third largest greenhouse gas (GHG) emitting industrial sector''
Vulcanization
Oil Refinary
Labor process
Monoculture Growing Techniques