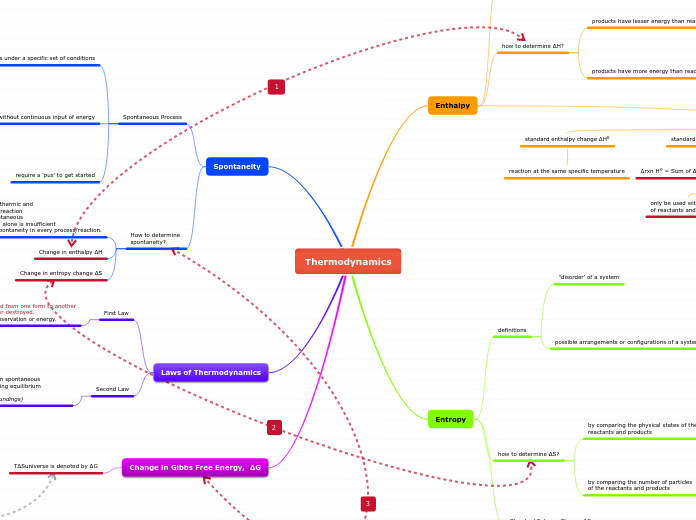
Thermodynamics
Type in the name of your subject.
Change in Gibbs Free Energy, ΔG
TΔSuniverse is denoted by ΔG
Laws of Thermodynamics
Second Law
the entropy of the universe increases in spontaneous processes and remains unchanged during equilibrium processes.
(∆S universe = ∆S system + ∆S surroundings)
spontaneous process,
∆S universe = + ve
ΔG = ∆H system - T∆S system
equilibrium process,
∆S universe = 0
First Law
energy can be converted from one form to another
but cannot be created or destroyed.
Based on the law of conservation or energy.
Spontaneity
Add detailed notes about each lecture, so that when the time comes to prepare for exams, you will have an easier and quicker overview.
How to determine
spontaneity?
Change in entropy change ΔS
Change in enthalpy ΔH
- both endothermic and
exothermic reaction
can be spontaneous
- sign of ∆H alone is insufficient
to predict spontaneity in every process/reaction.
Spontaneous Process
require a 'pus' to get started
Add a list of questions to help you recap your lecture.
occurs without continuous input of energy
Write down if there are things you would like to discuss or clarify with your teacher or colleagues in relation to this topic.
spontaneous
ball moving down a slope
non-spontaneous
water freezing at 25 °C 1 atm
occurs under a specific set of conditions
Add a short description of the lecture.
Entropy
Review your resource requirements and tick off the devices you will need as well as their availability. Add others, if necessary.
Standard Entropy Change ΔS
Add other resources:
∆rxnS = S (product) - S (reactant)
how to determine ΔS?
by comparing the number of particles
of the reactants and products
decrease in the number of particles
increase in the number of particles
by comparing the physical states of the
reactants and products
gas to solid
decrease in the number of possible arrangements
solid to gas
increase in the number of possible arrangements
definitions
Select as needed:
possible arrangements or configurations of a system
Examples
least number of possible outcomes
solid state
most number of possible outcomes
gaseous state
"disorder' of a system
Enthalpy
Type in all the info you would like to know about this subject. If there is something you don't know yet, no problem! You can fill in the blanks along the way.
Standard Enthalpy Change
Did your teacher present the objectives of this course? Write them down and add anything else that might help you reach these objectives.
standard bond dissociation
enthalpy
bond forming
energy released
ΔH bond forming is -ve
bond breaking
energy is absorbed
ΔH bond breaking is +ve
standard enthalpy change
of formation, Δf H°
Δf H° of an element &
7 diatomic elements
(H2, N2, O2, F2, Cl2, Br2, l2)
Δf H° = 0 kJ/mol
one mole of compound is formed from
its element in their reference states
standard enthalpy of reaction, Δrxn H°
∆rxn H° = Sum of Δf H° (product) - Sum of Δf H° (reactant)
unit of Δrxn H° is kJ
only be used with the Δf H°
of reactants and products
standard enthalpy change ΔH°
reaction at the same specific temperature
how to determine ΔH?
Type in the name of your teachers and teacher assistants, plus any details you should know about them.
products have more energy than reactants
Heat absorbed to
surroundings
endothermic reaction
+ve ΔH
products have lesser energy than reactants
Heat released to
surroundings
exothermic reaction
-ve ΔH
definition
Add details about your course.
Enthalpy change ΔH
- amount of heat released or absorbed
by a chemical system when a chemical
reaction occurs at constant pressure.