Topic flotante
Bibliografy: Borja G. Cosio, Rodriguez J, Rosado, y Fiorentino F. Asthma: Epidemiology, Pathophysiology, and Risk Factors Clinical Respiratory Medicine, Chapter 38, 487-500. Río B. Navarro E. Castro M. Sierra J. Asthma. Departamento de Alergia, Hospital Infantil de México Federico Gómez, México, D. F., México. Vol 66.
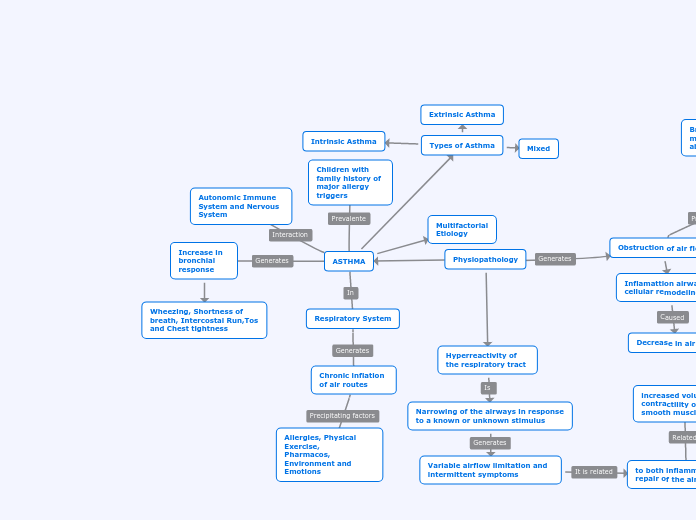
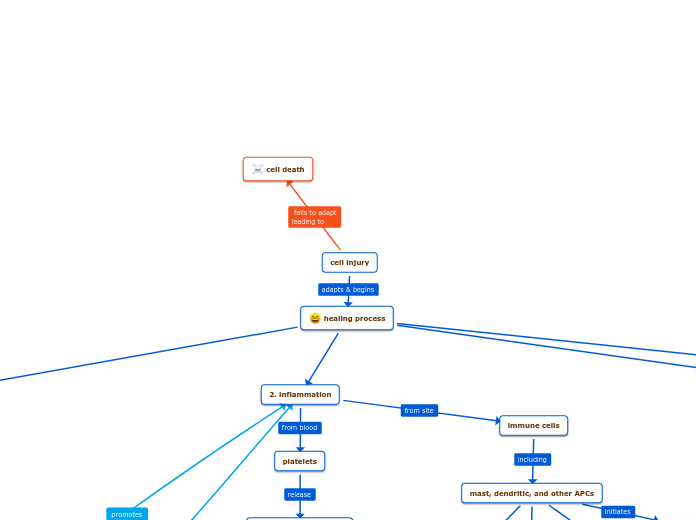
Physiopathology
Hyperreactivity of the respiratory tract
Narrowing of the airways in response to a known or unknown stimulus
Variable airflow limitation and intermittent symptoms
to both inflammation and repair of the airways
increased volume or contractility of smooth muscle cells
excessive airway contraction due to inflammatory changes
Response to sensory stimuli in sensory nerves sensitized by excessive inflammation
Obstruction of air flow
Inflamattion airway by cellular remodeling
Decrease in air flow
Increase in smooth muscle
Release of fibrogenic growth factors
There’s a deposit of collagen and elastolysis.
Bronchoconstriction: Abnormal smooth muscle contraction of the airways, intrinsic abnormality in the airway myocytes
Release of Acelticolin
Regulation of bronchial tone cells and proinflammatory cells
Airway Edema
Hypersecretion of mucus
Bronchial mucus plugging
Hypertrophy and cellular hyperplasia
ASTHMA
Types of Asthma
Mixed
Extrinsic Asthma
Intrinsic Asthma
Children with family history of major allergy triggers
Multifactorial Etiology
Autonomic Immune System and Nervous System
Increase in bronchial response
Wheezing, Shortness of breath, Intercostal Run,Tos and Chest tightness
Respiratory System
Chronic inflation of air routes
Allergies, Physical Exercise,
Pharmacos, Environment and
Emotions