Adaptation
It´s a complex process that has its theoretical root in Biology. It envolves modification of the individual or the environment to fit the needs of the individual.
Theoretical Rationale Construtivism
Theorical model that emphasizes the active role of the subject in their own learning.
Knowledge construction results from the interaction between the person and the environment in a systematical way.
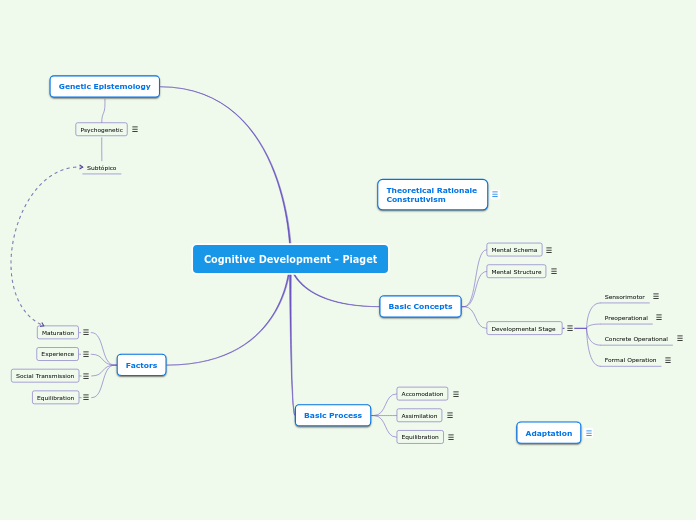
Cognitive Development - Piaget
Factors
It´s the most important factor because it plays an integrative role as well as a motivational one.
Social Transmission
Occurs when information, attitudes and customs are transmitted from group (parents) to another (children).
Experience
Includes physical and logical experience that results from the interaction between the person and changing environments and demands.
Maturation
The process throught which biological change takes place, controlled by innate mechanisms.
Genetic Epistemology
Psychogenetic
Method that provides the ontogenetic evolution of knowledge.
The genesis of intellectual strutures.
Subtópico
Basic Process
Equilibration
It is a self regulation process. It is the primary motivating force behind development.
Assimilation
It is the process through which the organism incorporate experiences into already existing schema.
Accomodation
It is a process of modifying existing schemata to satisfy the requirements of new experiences. It is a process through which new schema are formed.
Basic Concepts
Developmental Stage
Time required to construct a mental structure.
Formal Operation
Abstract thought
Concrete Operational
Concrete logical intelligence
Preoperational
Simbolic intelligence
Sensorimotor
Practical Intelligence
Mental Structure
A developing child builds cognitive structures for understanding and responding to external experiences within their environment.
A cognitive structure increases in sophistication with development, moving from a few innate reflexes such as crying and sucking to highly complex mental activities.
Mental Schema
It´s a primary unit of mental organizations.
A mental schema is an internal representation that comes from the abstraction and simplification of the external reality, it’s built on previous experiences and knowledge. When the experiences confirm our mental model, we take in this new information or experiences and incorporate them into our existing ideas.