Finish
Congratulations Guest! You are done.
You could do the following steps:
- Print this map out, take it with you and quickly rehearse before you begin your interview at Gestión del aprovisionamiento
- Save this map and come back later to refine it
Good luck with your interview!
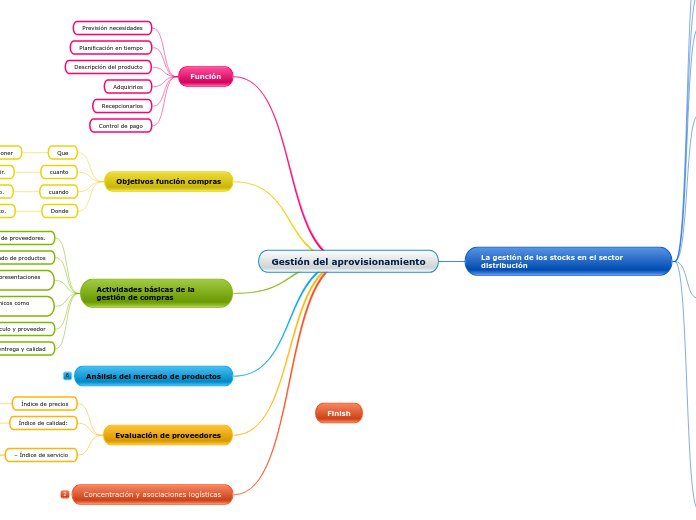
Gestión del aprovisionamiento
Type in the name of the company you are going to have an interview with.
Concentración y asociaciones logísticas
Ventajas globales
Centralización de las compras.
– Marketing.
– Publicidad y promociones
Evaluación de proveedores
– Índice de servicio
Subtopic
: (piezas entregadas en plazo/Total piezas solicitadas)
Índice de calidad:
(lotes aceptados/Lotes servidos)
Índice de precios
(precio más bajo ofertado/precio medio del mercado)
Análisis del mercado de productos
Aspectos legales.
Reglamentaciones gubernamentales,
– Régimen fiscal y aduanero.
º Presentaciones, costos de transportes y embalajes
Precios.
Consumo y distribución del producto.
Definición de nuestra necesidad en términos cualitativos y cuantitativos.
Actividades básicas de la gestión de compras
How ambitious are you?
Analizar variaciones en precio, plazos de entrega y calidad
Planificación de pedidos por artículo y proveedor
Previsión de compras en sus aspectos tanto técnicos como económicos y financieros.
Negociación permanente de precios, calidades, presentaciones y plazos de entrega,
Where and how do you see yourself in 5 years time?
Type in the answers.
Mantenimiento de un archivo actualizado de productos
What are your long-term goals ?
Type them in.
Evaluación y clasificación de proveedores.
What are your short-term goals ?
Type them in.
Short-term goal
Objetivos función compras
Donde
Hay que situar el producto.
cuando
What experience have you got from your previous jobs? Make sure you specify all your previous work experience, part-time jobs, vacation jobs, voluntary work, and unpaid work experience that are relevant for the position you are applying for.
Hay que efectuar el pedido.
cuanto
Describe a typical work day in your previous/current position.
Cantidad hay que comprar o adquirir.
cantidad hay que comprar o adquirir.
Que
Why will/did you leave your existing/last job?
Productos hay que reponer
Función
Do you fully understand what this position implies?
After you've made some research on the company, read the job description thoroughly, and try to fully understand what your responsibilities will be.
Control de pago
Recepcionarlos
Adquirirlos
Descripción del producto
What would you do on the first day?
What about the first week(s)? Fill in some of the actions that you are planning to take.
Planificación en tiempo
What do you think the main challenges will be?
Type them in.
Previsión necesidades
What will be your main tasks?
Type them in.
La gestión de los stocks en el sector distribución
Research the company
You should find and learn as much as you can about the company where you are having an interview.
The interviewer will want to see what you know about them and why you chose the company.
Doing your homework will show that you are really interested.
SISTEMAS DE REPOSICIÓN
. Principales ventajas del D.R.P
El sistema D.R.P. permite mantener la mayor parte de los stocks de seguridad en el
almacén central, con lo cual se consigue una economía de escala en la utilización de los
stocks
Sistema DRP
Su lógica de cálculo se basa en los siguientes principios:
En un punto central (normalmente el centro de distribución) se mantiene un registro a
nivel de “ítem” (referencia comercial) y almacén de todos y cada uno de los productos objeto
de distribución,
(Distribution Requirement Planning)
D= Consumo de la demanda durante el período de aprovisionamiento.
L=Tiempo de Aprovisionamiento del producto (lead-time).
Qs = Stock de seguridad requerido.
PUNTO ESTADÍSTICO DE PEDIDOS
El doble punto estadístico de pedidos (D.O.P.)
La demanda debe ser constante, conocida, regular y de fácil predicción.
Cálculo de los costes de posesión
Sistemas de reposición de stocks
Cálculo del stock normativo global.
– Política de ubicación de los stocks.
– Sistemas de almacenaje y distribución física.
Consideraciones sobre los modelos de decisión para
medir los stocks
Los cálculos básicos para generar la norma de stocks se efectúan a nivel de ítem o
referencia comercial tomando un historial de un año
º Los parámetros necesarios para el cálculo del stock base, nivel de servicio, stock de
seguridad, etc.
Los cálculos se orientan a nivel “familia de productos
Riesgos
Los costes de riesgos se relacionan con las pólizas de seguro que hay que pagar por las
mercancías ubicadas
Costes de almacenamiento
el coste de almacenamiento de un producto dependerá de las características
físicas del mismo: volumen, empaquetado, medio de contención empleado (pallet,
contenedor, etc.)
Cálculo de los costes de interés del capital vinculado a los stocks
Tasa de interés pagada.
– Nivel promedio del stock a lo largo del año.
– Nivel de precios de coste de los stocks
Calculo Stock
Calculo de lso stocks
Stock base = (Plan anual aprovisionamiento/Frecuencia Aprovtº)/2
STOCK NORMATIVO = STOCK BASE + STOCK DE SEGURIDAD
otras clases de Stocks
Stocks para atender “pedidos especiales”.
– Stocks clasificados como administrativos (tales como stocks para reparar,
consignaciones y obsolescencia de productos).
El stock que no contribuye a conseguir el G.S.I.
What products does this company have?
Type in several examples.
Stock en tránsito.
• Otros stocks no disponibles.
El stock que proporciona el G.S.I.
What is the size of this company?
Stock base.
• Stock de seguridad.
• Stock de infraestructura.
El concepto de norma de stocks
What can you do for this company that someone else can't?
Type in several unique traits that will turn you into the perfect candidate for the position.
Los stocks son un medio, no una meta
El concepto de stock normativo
el nivel de stocks que en términos de promedio tiene que mantener una
empresa para dar un grado de servicio óptimo desde el punto de vista de costes
totales.”
El concepto de rotación y cobertura de stocks
What do you know about the company?
Type a short description of the company's background.
número de veces que un artículo se renueva en el almacén al cabo de un año
O sea: ROTACIÓN = VENTA ANUAL/STOCK PROMEDIO
Clasificación operativa y funcional de los stocks
Why do you want to work for this company?
Think of what you can do for them, not of what they can do for you.
Stock comercial.
Stock de productos terminados, situados en los almacenes comerciales y a
disposición de la venta.
Stock industrial
Materias primas y componentes.