Light and Geometric Optics
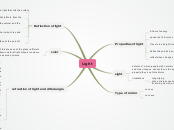
Reflection of Light
Law of Reflection
Specular reflection
Reflection of light off a smooth surface
The incident ray, reflected ray, and the normal
all lie in the same plane
Angle of Incidence = Angle of Reflection
Light
Speed of Light
Vacuum
3.00 X 10⁸ m/s
Production of Light
Light-Emitting Diode
Light produced by an electric current
flowing in semiconductors
Triboluminescence
The production of light as a result
of friction
Bioluminescence
The production of light in living
organisms without producing heat
Chemiluminescence
The production of light as a
result of a chemical reaction
Fluorescence
The immediate emission of light as a result of
ultraviolet light
Phosphorescence
Light production through the absorption of
ultraviolet light resulting in emission of visible
light
Electrical Discharge
Light production by passing an
electric current through gas
Incandescense
The production of light as
a result of high temperature
Electromagnetic radiation that does not
require a medium of transmission
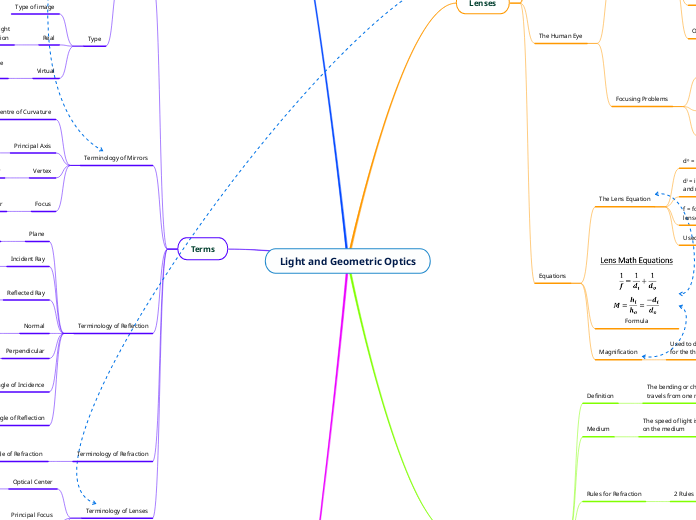
Terms
Terminology of Lenses
Emergent Ray
The light ray that leaves a lens after refraction
Principal Focus
The point on the parallel axis where light rays
parallel to the principal axis converge after refraction
Optical Center
Point at the exact center of the lens
Terminology of Refraction
Angle of Refraction
The angle between the refracted ray
and the normal
Terminology of Reflection
Angle of Reflection
The angle between the reflected ray
and the normal
Angle of Incidence
The angle between the incident
ray and the normal
Perpendicular
At right angles
Normal
The perpendicular line to a
mirror surface
Reflected Ray
The ray that bounces off a reflective
surface
Incident Ray
The incoming ray that hits a surface
Plane
Flat
Terminology of Mirrors
Focus
The point at which light rays parallel to the
principal axis when they are reflected off the mirror
Vertex
The point where the principal axis meets the mirror
Principal Axis
The line through the center of
curvature to the midpoint of the mirror
Centre of Curvature
The center of the sphere whose surface has
been used to make the mirror
SALT
Type
Virtual
Image formed where light does not arrive
at image location
Real
Image formed when light
arrives at image location
Type of image
Location
Location of the image
Attitude
Is the image upright or inverted
Size
The size of the image
Characteristics used to describe the
properties of an image
Mirrors
A mirror shaped like part of the surface
of a sphere in which the inner surface is reflective
A mirror shaped like part of the surface
of a sphere in which the outer surface is reflective
How to Locate Image in Mirrors
Convex
A ray aimed at the focus is reflected
parallel to the principal axis
A ray aimed at the center of curvature
is reflected back upon itself
A ray parallel to the principal axis is reflected
as if it had come through the focus
Concave
4 Rules
A ray aimed at the vertex will follow the law of reflection.
A ray through F will reflect parallel to the principal axis.
A light ray through the center of curvature is reflected
back onto itself. The reflected ray will return on the same path.
A light ray through the principal axis
is reflected through the focus
Refraction of Light
Total Internal Reflection
Critical Angle
The angle of incidence that results in
an angle of refraction of 90 degrees
If you increase the angle of incidence past the Critical Angle
the refracted ray will no longer exit the medium, instead, only a reflected ray is visible.
The Index of Refraction
n = sin i/sin R
n = C/V
The ratio of the speed of light in a vacuum to the speed of light in a medium.
Rules for Refraction
2 Rules
Light bends towards the normal when the speed of light in the second medium is less than in the first medium. Light bends away from the normal when the speed of light in the second medium is greater.
The incident ray and reflected ray all lie in the
same plane. The incident ray and the reflected ray are on opposite sides of the line that separates the two media.
Medium
The speed of light is different depending
on the medium
Definition
The bending or change in direction of light when it
travels from one medium into another
Lenses
Equations
Magnification
Used to determine the magnification of a lens
for the thin lens equation.
Formula
The Lens Equation
Used to easily determine the image characteristics
f = focal length and is positive for converging
lenses and negative for diverging lenses
dⁱ = image distance and is positive for real images
and negative for virtual images.
dᵒ = object distance and is always positive
The Human Eye
Focusing Problems
Myopia
The inability of the eye to focus light from distant objects.
Presbyopia
A form of far-sightedness caused by a loss
of accommodation as a person ages.
Hyperopia
The inability of the eye to focus light from
near objects.
Parts of the Eye
Optic Nerve
The optic nerve transmits electric signals from the
retina, and creates a blind spot in the back of each eye.
Retina
Converts light signals into electrical signs that is
then transmitted to the brain through the optic nerve.
Cornea
Light is refracted through the cornea.
Pupil
Where light enters the eye.
Iris
Colored part of the eye that opens and closes
to let in more or less light.
Diverging Lens
A lens that is thinnest in the middle and that
causes incident parallel light rays to spread apart after refraction
Converging Lens
A lens that is thickest in the middle and that
causes incident parallel light rays to converge through
a single point after refraction
Images in Lenses
How to Locate the Image in a Diverging Lens
A ray through the optical center continues
straight through without being refracted
A ray that appears to pass through the secondary principal focus is refracted parallel to the principal axis.
A ray parallel to the principal axis is refracted
as if it had come through the principal focus.
How to Locate the Image in a Converging Lens
3 Rules
A ray through the optical center continues
straight through without being refracted.
A ray through the secondary principal focus
is refracted parallel to the principal axis.
A ray parallel to the principal axis is
refracted through the principal focus