Educational Theory &
Online Learning
Behavior Theory
Theorists: Thorndike, Pavlov, Skinner
Teach WHAT, focuses on facts
Learning is a change of observable
behavior caused by external stimuli.
Connectivist Theory
Design learning for machines and humans.
The integration of principles explored by chaos,
network, complexity, and self-organization. The
key idea is we must be able and willing to LEARN,
UNLEARN, and RELEARN.
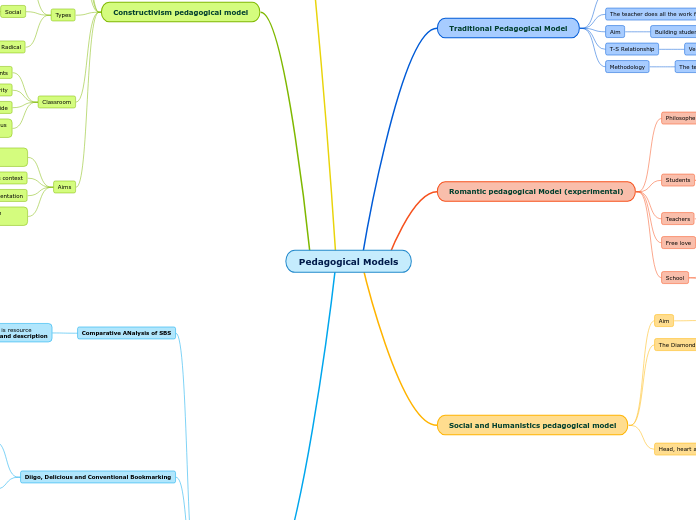
Constructivist Theory
Interaction: Learning should be interactive
Personal Meaning
Social Presence
Higher Level Learning
Transformative Learning: (Mezirow)
reflectively transforming the beliefs,
attitudes, opinions and emotional reactions
that constitute meaning.
Learners interact with content, other
learners, and instructors to test and
confirm ideas, applying what was learned
Situated Learning: The belief that
learning is contextual
Teach WHY, focuses on higher-level thinking skills.
Learners interpret the world based on
their own personal reality. We learn
through observation, processing, and
interpretation. We then personalize it.
Cognitive Theory
Learning Style: How learners perceive, interacts with and responds to the learning environment. Can be determined through different measures.
Metacognition: The learner's awareness of their own learning capabilities and be able to use that to learn effectively.
Motivational Theory: Learners should be
motivated to learn.
ARCS Model (Keller): a model that
addresses how to motivate learners
during learning.
Satisfaction: Provide feedback
Confidence: Build confidence by
moving from simple to complex/
known to unknown. Use objectivites.
Relevance: Benefit of learning
Attention: Catch and moviation
Extrinsic Motivation
Intrinsic Motivation
Dual Coding Theory (Paivio) Information
presented in different modes will be better
processed. Information processed in
different parts of the brain means more
encoding. Better memory!
COGNITIVE STYLE: The learner's preferred
way of processing information. It is an
individual different indicator.
Field-dependent and Field-Independent
It is a personality factor that
influences attitudes, values,
social interaction.
Strategies should be used in consideration
of attention and perception.
Teaches HOW, focuses on processes and principles.
Based on cognitive psychology. Learning
involves the use of memory, motivation,
and thinking. Reflection is a crucial
component of learning.