por Anna mariz Bonde hace 7 años
990
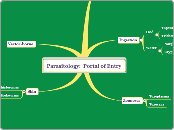
Plant Physiology
Plants maintain a delicate balance of water and nutrients through a series of sophisticated mechanisms. These mechanisms include the detection and response to environmental changes, such as variations in water availability and nutrient levels.