por jaminton ordoñez hace 1 año
164
Present progressive
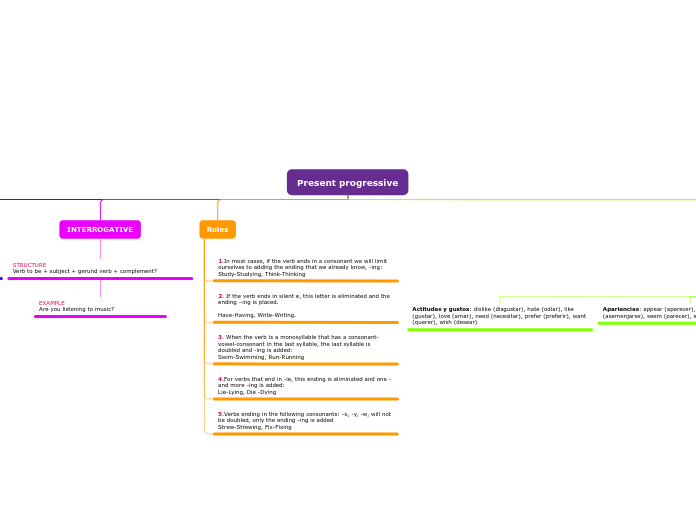
In English, the present continuous tense is used to describe ongoing actions. Specific rules govern how verbs are conjugated in this tense. For verbs ending in a silent 'e,' the 'e'
por jaminton ordoñez hace 1 año
164

Ver más